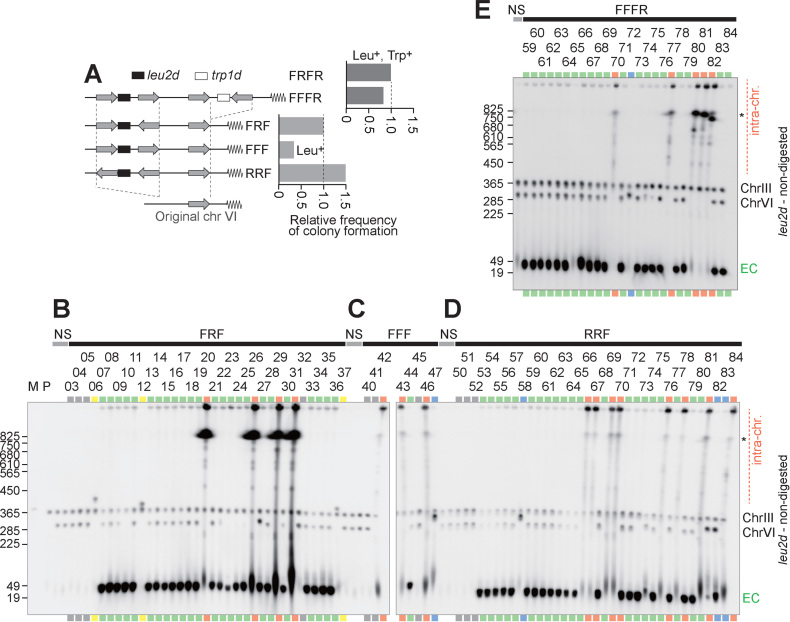
Figure 4.
Analysis of amplification products from variants of repeat structure. (A) Schematic structures of FFFR, FRF, FFF and FRFR constructs. The leu2d and trp1d genes are amplification markers. A 3.1-kb genomic sequence (gray arrow) was PCR-amplified to construct IR structures. The frequency of Leu+ (for FR) or Leu+Trp+ (for FRFR) colony formation was plotted. (B–E) Southern blots of chromosomal DNA from FFFR (B), FRF (C), FFF (D) and RRF (E). The samples marked in red and green indicate intra- and extra-chromosomal products, respectively. The gray lanes showed no sign of amplification, suggesting Leu+ recombination between the leu2d marker and the mutated original leu2 allele on chr III. The blue samples suggest moderate copy number increase of the leu2d gene likely through unequal sister chromatid exchange. The yellow samples possibly contain a fusion between chromosome VI and III, which cause Leu+ recombination between the leu2d marker and the mutated original leu2 allele on chr III. Black asterisks on the right side of panels indicate separation limit under the PFGE-condition. M: S. cerevisiae marker; P: the parental strain, LS20; NS: non-selective conditions; EC: extra-chromosomal products.