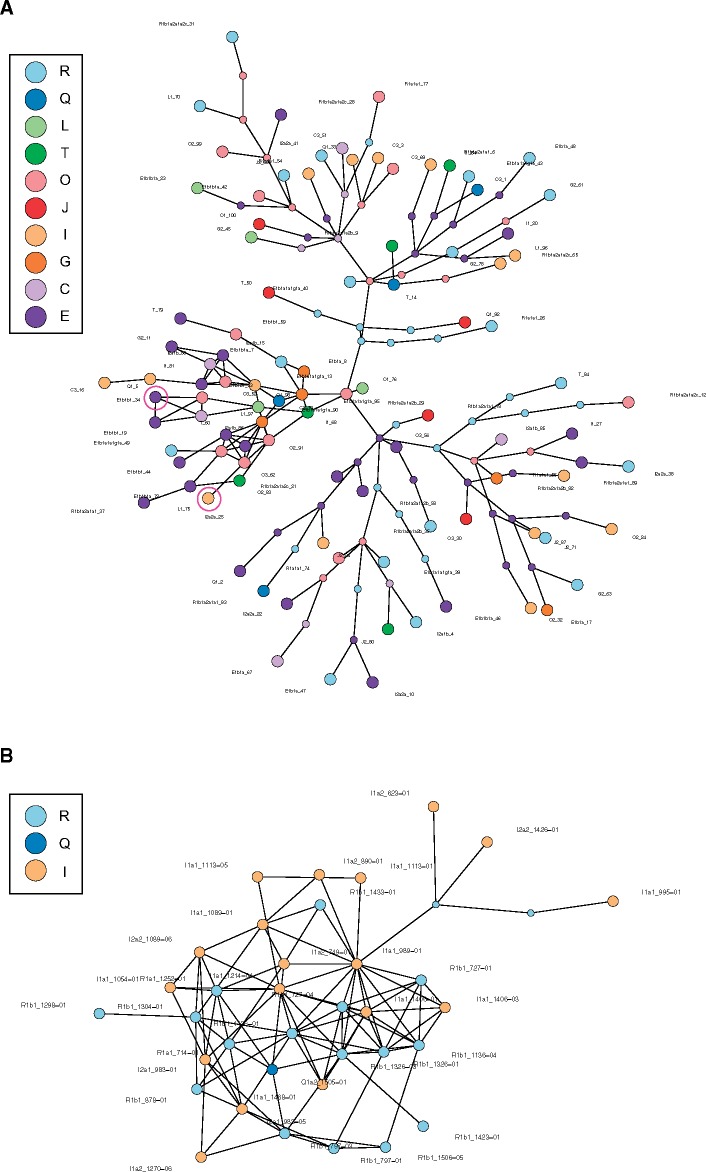
Fig. 7.
—(A) Haplotype network constructed based on a pairwise distance matrix constructed from the alignment of 100 strings of nine groups of characters corresponding to copy numbers of nine ampliconic gene families for 100 males (98 haplotypes; rounded copy number values were used; supplementary table S3, Supplementary Material online). Each big colored disc represents a different haplotype. Small colored discs represent intermediate haplotypes. Black lines connect each haplotype to its closest relative. A link between two haplotypes corresponds to a one-copy difference in one gene family. If extant or ancestral haplotypes are joined by several consecutive links, this indicates several copy number differences (either within the same or different gene families) between them, and the number of such links corresponds to the number of copy number differences. Pink rings indicate haplotypes that were observed in more than one individual. (B) Same as A, but for the data from 62 Danish males in (Skov et al. 2017; rounded copy number values were used; supplementary table S5, Supplementary Material online).