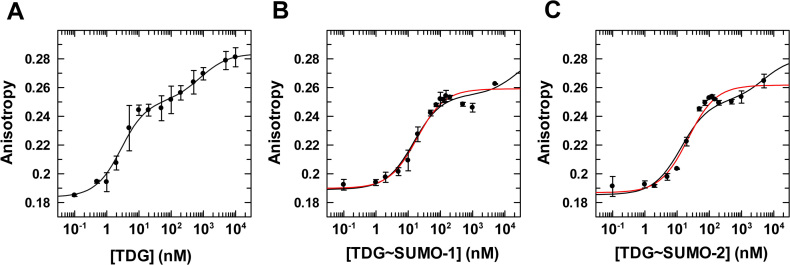
Figure 7.
Equilibrium binding of TDGN140A, unmodified and sumoylated, to G·caC DNA (1 nM) monitored by fluorescence anisotropy. (A) Data for TDGN140A binding to G·caC DNA, fitted to a two-site model (using Dynafit), gives Kd = 2.3 ± 0.6 nM, Kd2 = 820 ± 500 nM, rD= 0.184 ± 0.0033, rED = 0.251 ± 0.004, and rEED = 0.284 ± 0.004. (B) Binding of TDGN140A∼SUMO-1 to G·caC DNA fitted to a two-site model (black line) gives Kd = 14 ± 2 nM, Kd2 = 24000 ± 16000 nM, rD= 0.189 ± 0.002, rED = 0.255 (fixed), and rEED = 0.285 (fixed). Fitting to a one site model (red line) yields essentially the same affinity, Kd = 16 ± 3 nM, with rD = 0.190 ± 0.002, and rED = 0.257 ± 0.002. (C) Binding of TDGN140A∼SUMO-2 to G·caC DNA fitted to a two-site model (black line) gives Kd = 13 ± 2 nM, Kd2 = 5000 ± 2000 nM, rD = 0.185 ± 0.003, rED = 0.251 (fixed), and rEED = 0.281 (fixed). Fitting to a one site model (red line) yields Kd = 20 ± 3 nM, with rD = 0.187 ± 0.002, and rED = 0.260 ± 0.002. Fitting for TDG∼SUMO-1 and -2 employed fixed values for rED and rEED, using the same approach described for fitting binding of these enzymes to G·fC DNA (Figure 6).