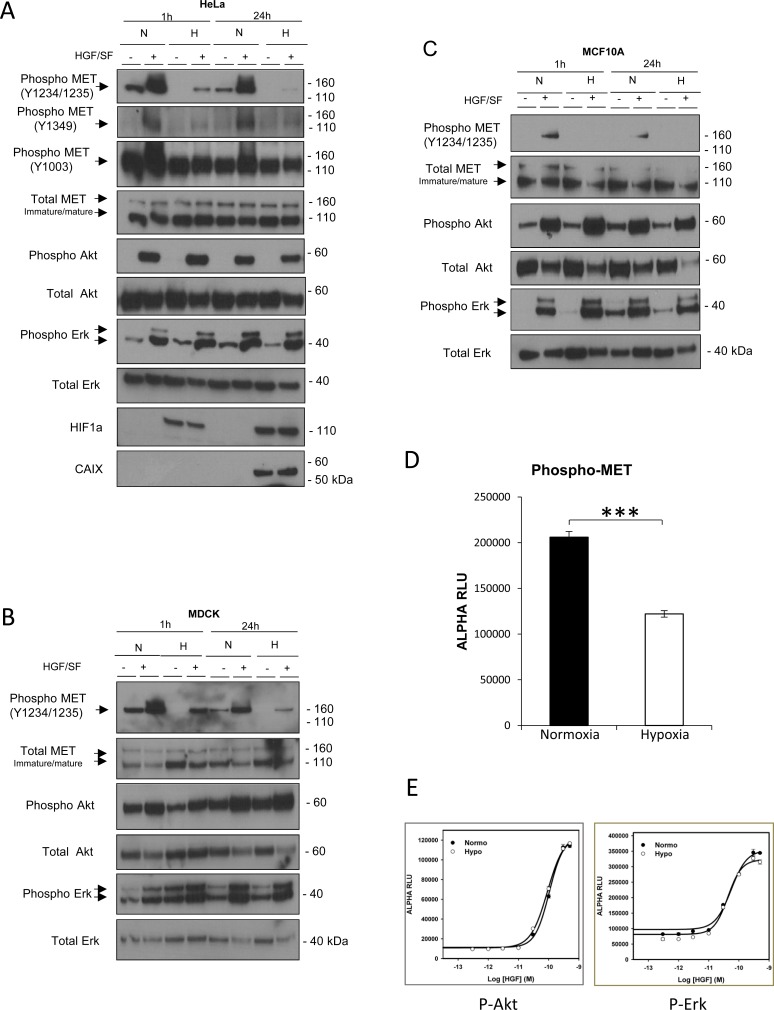
Figure 1. Effect of hypoxia on MET phosphorylation and activation of the Akt and Erk downstream pathways.
Hela (A), MDCK (B), and MCF10A (C) cells were incubated for 1 or 24 h under normoxic or hypoxic conditions and then treated or not for 10 minutes with 10 ng/mL HGF/SF. For each cell line, the same amount of protein was analyzed by western blotting with antibodies directed against the indicated phosphorylated residue(s) in the MET kinase domain, juxtamembrane domain, or C-terminal domain or against one of the following: the MET kinase domain, phosphorylated Akt, Akt, phosphorylated Erk, Erk2, or the hypoxia marker HIF1a or carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX). The positions of prestained molecular weight markers are indicated. Arrows indicate the positions of precursor and mature full-length MET and Erk1/2 proteins. (D) GTL16 cells were placed under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 1.5 h. Cell lysates were incubated for AlphaScreen specific phospho-MET quantitation. Error bars represent standard deviations (± SD). (E) MCF10A cells were placed under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 1.5 h, then treated for 10 minutes with HGF/SF at 50, 30, 10, 3, 1, 0.3, or 0 ng/mL. Cell lysates were incubated for AlphaScreen specific phospho-Erk and phospho-Akt quantitation. Error bars represent standard deviations (± SD).