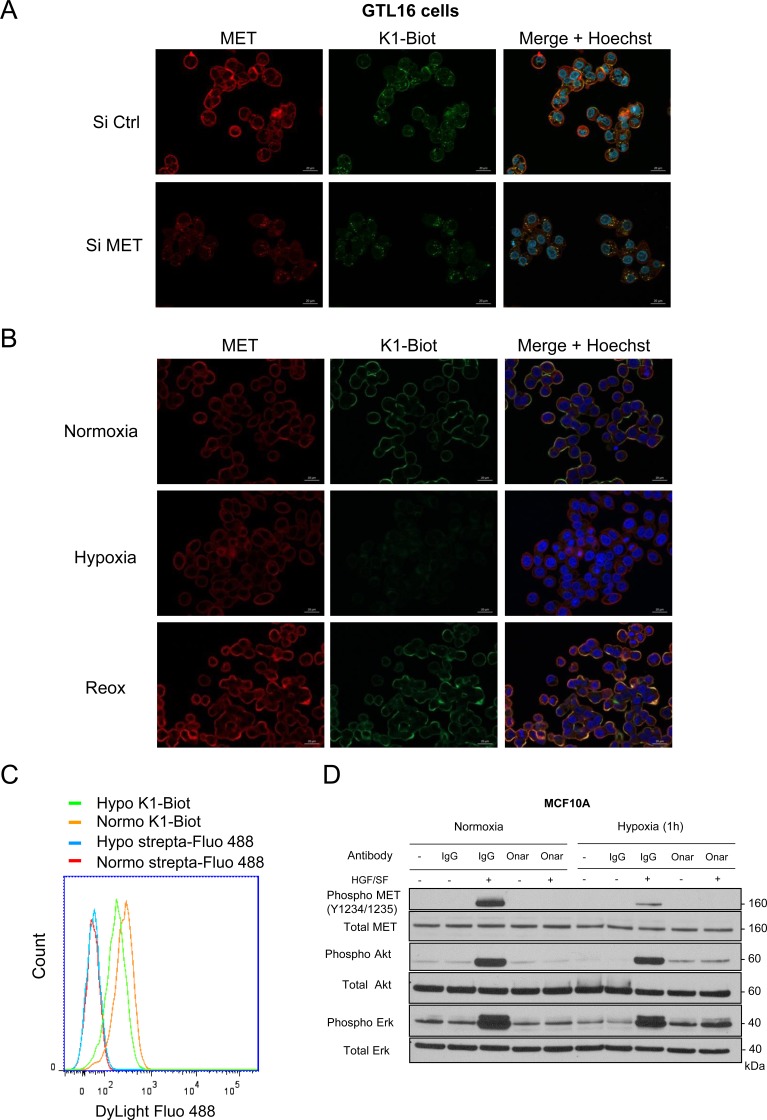
Figure 6. Interaction of K1 subdomain of HGF/SF with MET receptor.
(A) GTL16 cells were transfected with a pool of three MET-targeting siRNAs (90 nM) or a control siRNA (siCtrl) and grown on glass coverslips, (B) Cells were placed under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 2 h. Another set of cells were incubated under hypoxia for 2 h and then returned to normoxia for 2 h (re-oxygenation, Re-ox). (A, B) Cells were incubated 10 min with a complex K1-biotinylated/streptavidin-DyLight 488 (100 nM/50 nM respectively) (green staining, strepta-Fluo 488). Cells were then fixed and labeled with an anti-MET antibody recognizing the intracellular domain of the receptor (red staining) and their nucleus stained with Hoechst (blue staining). An overlay of the three stains is shown (merge) (scale bar = 20 µm). (C) Cells were placed under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 2 h and incubated 10 min with a complex K1-biotinylated/streptavidin-DyLight 488 (100 nM/50 nM respectively) or streptavidin-Dylight 488 alone and analyzed by flow cytometry. (D) MCF10A cells were placed under normoxia or hypoxia for 1 h and incubated with 10 μg/ml onartuzumab (Onar) or the corresponding human control IgG (IgG). Cells were then stimulated or not for 10 min with 10 ng/mL HGF/SF. The same amount of protein was resolved by 4–12% Bis-Tris SDS-PAGE and analyzed by western blotting with antibodies directed against phosphorylated residues of the MET kinase domain, the MET kinase domain, phosphorylated Akt, Akt, phosphorylated Erk, or Erk2. The positions of prestained molecular weight markers are indicated.