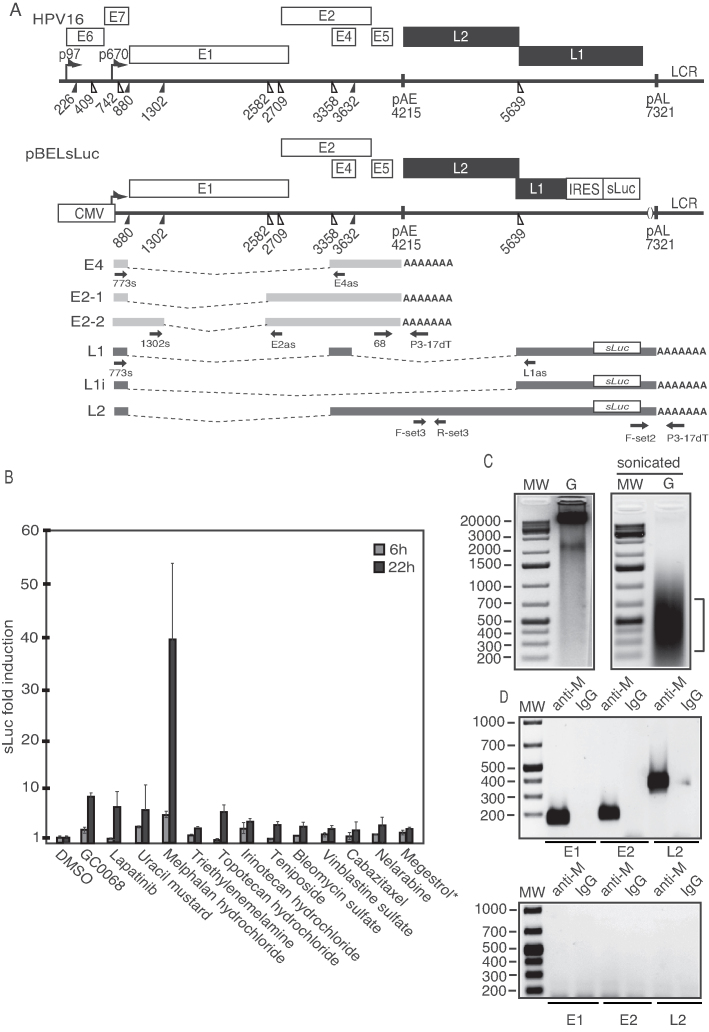
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the HPV16 genome. Rectangles represent open reading frames, promoters p97 and p670 are indicated as arrows, filled and open triangles represent 5′- and 3′-splices sites, respectively, HPV16 early and late polyA signals pAE and pAL are indicated. Below the HPV16 genome, a schematic representation of the pBELsLuc reporter plasmid stably integrated in the genome of the C33A2 cells (32,37). Transcription of the HPV16 sequences in the pBELsLuc plasmid is driven by the human cytomegalovirus promoter (CMV). The sLuc gene inserted into the L1 region is indicated and is preceded by the poliovirus 2A IRES. HPV16 E2 and E4 mRNAs mRNAs produced by C33A2 cells are indicated in light gray and HPV16 late mRNAs encoding sLuc that can be induced in this reporter cell line are indicated in black (See supplementary Table S3 for primer sequences). Arrows represent RT-PCR primers. (B) Fold induction of sLuc enzyme activity in the cell culture medium of reporter cell line C33A2 after incubation for 6 or 12 h with Akt-kinase inhibitor GDC-0068 (that has been shown previously to induce HPV16 late gene expression in C33A2 cells), or with the DNA-damaging cancer drugs lapatinib, uracil mustard, melphalan hydrochloride or triethylenemelamine. sLuc activity is displayed as fold over DMSO-treated C33A2 cells at the two time-points. *megestrol acetate. (C) Genomic DNA (G) extracted from melphalan-treated C33A2 cells before (left) and after (right) sonication. (D) PCR on sonicated DNA from C33A2 cells treated with melphalan (upper panel) or DMSO (lower panel) after immunoprecipitation of DNA with anti-melphalan antibody or IgG. Location of the PCR-primers in the HPV16 genome for amplification of the HPV16 E1, E2 and L2 regions are shown in Supplementary Figure S6 and primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Table S3.