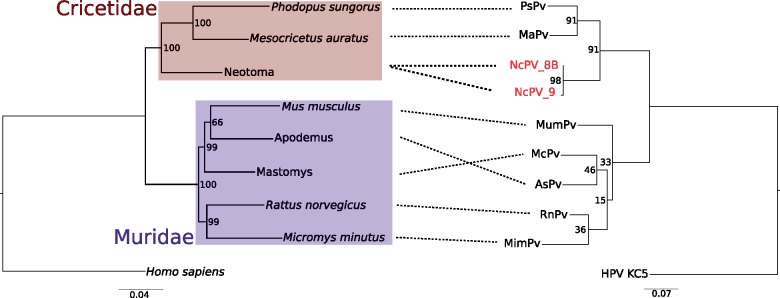
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic congruence of PVs (right) and their hosts (left). Relationships between host and virus are indicated by dashed black lines. The host phylogeny is inferred from five loci, while the PV phylogeny is based on a 287 bp alignment of a fragment of L1 with the third codon positions stripped. Both trees were inferred with RAxML 8.2.9. Number at nodes indicates bootstrap support based on one hundred replicates. Branch lengths are in expected number of nucleotide substitutions per site. For the PV phylogeny a related human PV (GenBank accession NC_026946) was used as an outgroup. On the host phylogeny, colored boxes indicate families of rodents from the superfamily Muroidea. For three of the host species, not all loci were available on GenBank and so sequences from a related species in same genus was downloaded and used. For these cases, instead of a host species name, the genus is given.