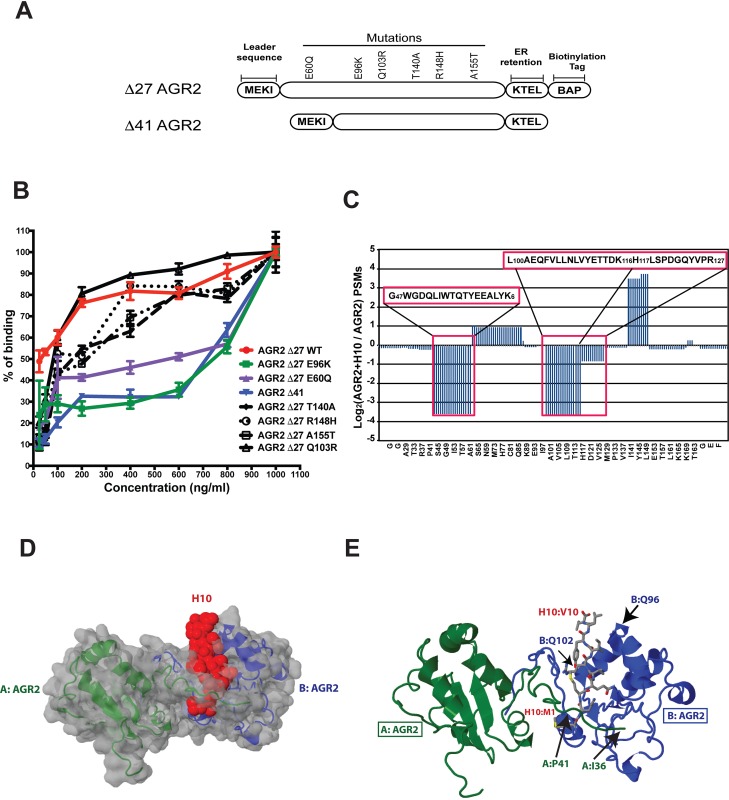
Figure 4. H10 binds AGR2 at two distinct sites.
(A) Schematic of AGR2 construct with location of mutations or truncations that were used to identify the binding interface of H10. (B) H10 ELISA with various AGR2 constructs to measure the relative binding. (C) Two distinct regions of AGR2 show protection from trypsin treatment upon pre-incubation with H10 followed by lysine-based cross-linking. Number of peptides score matches (PSMs) were determinate by bottom-up proteomics. Amino acid regions with loss of PSMs are highlighted in red boxes. (D) Structure of AGR2 dimer superimposed with the proposed H10 binding site by performing flexible docking simulations with the CABS algorithm. AGR2 molecules are colored green and blue. H10 space fill is colored red. (E) Specific amino acid contacts between H10 (red) and AGR2 (blue, green) highlight the potential binding interface as determined by mutagenesis, cross-linking, and docking.