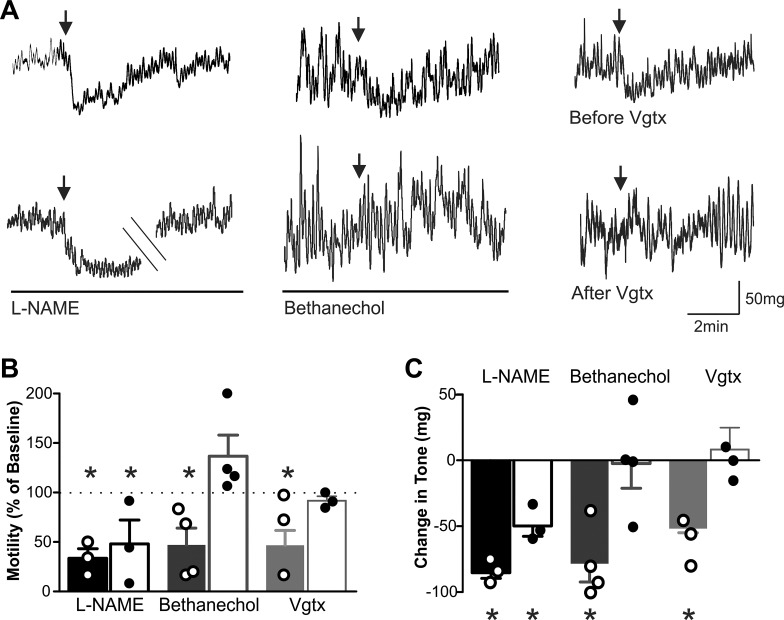
Fig. 6.
Brainstem microinjection of N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists inhibits gastric motility and tone in a vagally dependent manner involving the efferent cholinergic pathway. A: representative recordings demonstrating that the effects of dorsal vagal complex (DVC) microinjection of kynurenic acid (100 pmol/60 nl; top) are blocked by complete subdiaphragmatic vagotomy (Vgtx; right) and infusion of bethanechol (30 μg·kg−1·0.5 ml−1; middle) but not by infusion of nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME) (10 mg·kg−1·0.5 ml−1; left). B: graphical summary of the effects of DVC microinjection of kynurenic acid on antrum motility before and after perfusion of l-NAME, perfusion of bethanecol, and complete subdiaphragmatic Vgtx, perfusion of l-NAME, and perfusion of bethanechol (n = 3–5 per data point; *P < 0.05 vs. baseline paired Student’s t-test). C: graphical summary of the effects of DVC microinjection of kynurenic acid on antrum tone, before and after complete subdiaphragmatic Vgtx, perfusion of l-NAME, and perfusion with bethanechol (n = 3–5 per data point; *P < 0.05 vs. baseline paired Student’s t-test).