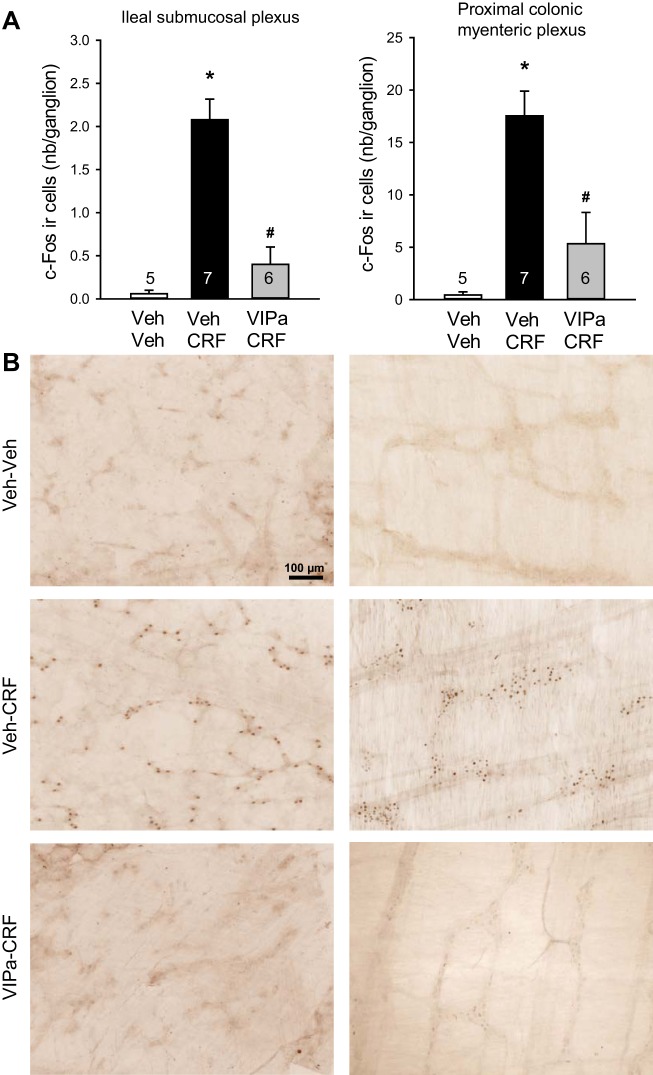
Fig. 5.
Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) antagonist reduces intraperitoneal corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)-induced increase in c-Fos immunoreactivity in the submucosal plexus of terminal ileum and myenteric plexus of proximal colon. Rats were injected intraperitoneally with vehicle (Veh: saline) or VIP antagonist (VIPa, 250 µg/kg) immediately before intraperitoneal CRF (10 µg/kg) or Veh (saline) and euthanized 1 h later for c-Fos immunohistochemistry. A: bar graphs are means ± SE of c-Fos-immunoreactive cell count per ganglion (average of 20/rat, and rat number is indicated at the bottom of each column). *P < 0.001 vs. Veh/Veh and #P < 0.005 vs. Veh/CRF (1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc multiple comparisons). B: representative photomicrographs of c-Fos-immunoreactive cells in the ileal submucosal plexus (left) and proximal colonic myenteric plexus (right). Scale bar = 100 µm.