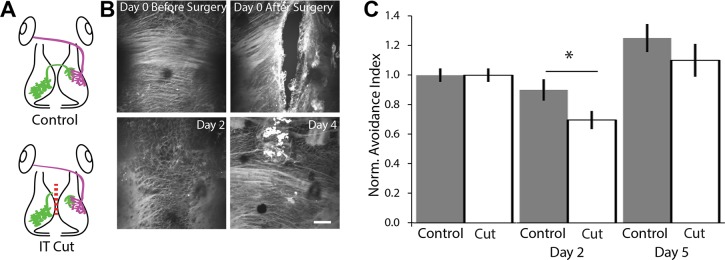
Fig. 1.
Intertectal commissure transection impairs visual avoidance behavior. A: schematic of experimental groups. Tadpoles received sham surgery (control) or surgery in which the intertectal (IT) commissure was transected (IT cut). Green axons, intertectal; magenta axons, retinotectal. B: in vivo confocal images of FM 4-64-labeled intertectal axons before and after surgery. Axons were completely cut. Axon regeneration occurs over 4 days after surgery. Scale bar: 50 µm. C: cutting the IT commissure impairs visual avoidance behavior. Data are presented as an avoidance index: the number of times over 10 encounters that a tadpole avoids an anticipated collision, normalized to baseline before surgery (day 0). Tadpoles with cut IT axons had a deficit in avoidance behavior 2 days after surgery. Tadpoles recover avoidance behavior comparable to sham controls after 5 days. Data are means ± SE on day 0 (before surgery), day 2 (n = 36 control and 28 cut axons; *P = 0.042), and day 5 (n = 18 control and 17 cut axons). A 2-tailed Student’s t-test was used to determine significance. Norm., normalized.