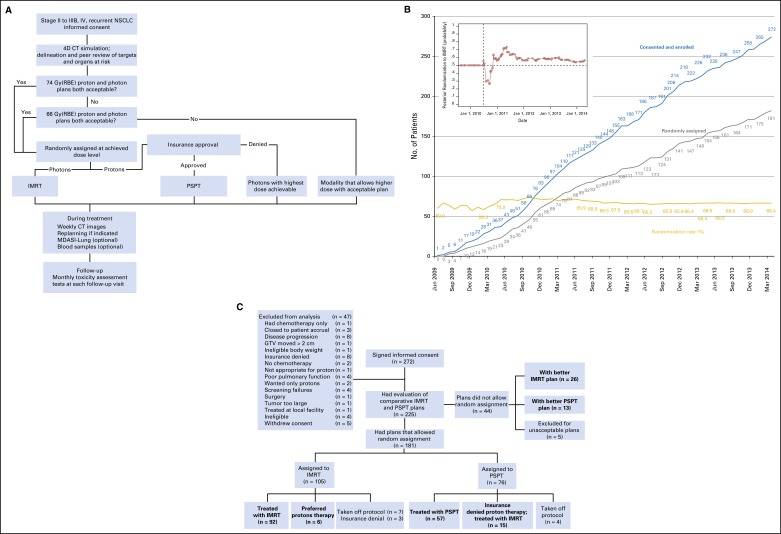
Fig 1.
(A) The adaptive randomization process. Eligibility criteria included stage II to IIIB non–small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), or stage IV NSCLC with a single brain metastasis or isolated tumor recurrence after surgical resection; 50% of patients had disease progression after systemic chemotherapy before enrollment. All patients underwent four-dimensional computed tomography (4D CT)–based treatment simulation; target volume contours and preliminary plans were reviewed before patients were randomly assigned. The prescribed dose for both sets of treatment plans (intensity-modulated [photon] radiation therapy [IMRT] and passive scattering proton therapy [PSPT]) was 74 Gy (relative biologic effectiveness [RBE]). If one of the two plans did not meet prespecified dose constraints (Data Supplement), the prescribed dose was reduced to 66 Gy for a second pair of plans. Patients were randomly assigned only when both IMRT and PSPT plans met dose constraint standards. If one of the two plans did not meet dose constraints at 66 Gy(RBE), the patient was treated with the modality that produced the acceptable dose distribution. During treatment, weekly 4D CT scans were obtained for all patients and additional treatment plans were created as needed to account for anatomic changes. Patients were contacted weekly with a questionnaire to assess symptoms of pneumonitis to ensure that radiation pneumonitis events (toxicity assessment) were accurately noted. (B) Cumulative patient random assignment and enrollment over time. The inset shows posterior randomization probability to IMRT, with the vertical dashed line representing the last date (June 22, 2010) at which the randomization probability was 0.5. The first patient was randomly assigned on August 17, 2009, and the last patient was assigned on April 18, 2014; 60% to 67% of all patients who consented to participate were eligible for random assignment. (C) Trial profile. The final numbers of patients included in the analysis are shown in boldface. GTV, gross tumor volume; Gy(RBE), the absorbed radiation dose, in Gy, multiplied by the relative biologic effectiveness factor (RBE) for protons; MDSAI, MD Anderson Symptom Inventory.