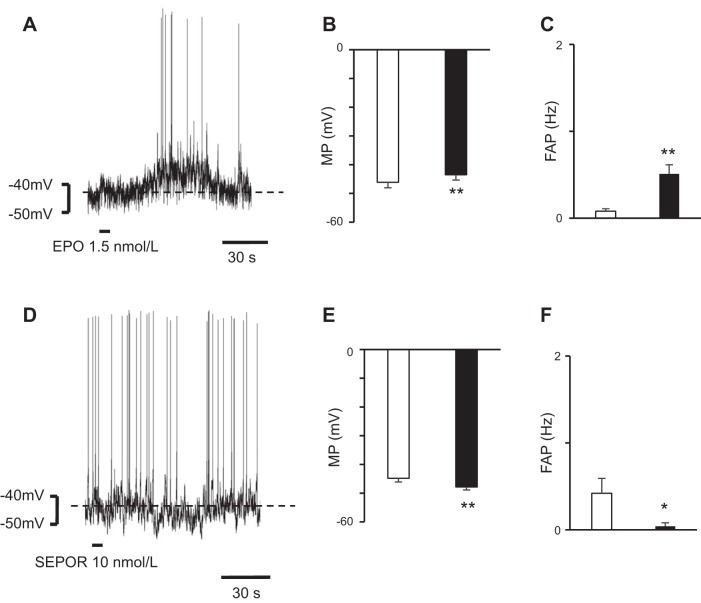
Fig. 4.
Change in membrane potentials (MPs) of intermediolateral cell column (IML) neurons after microsuperfusion with erythropoietin (EPO) or soluble erythropoietin receptor (SEPOR) over the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) area. A: IML neuron at the Th2 level was depolarized after EPO microsuperfusion over the RVLM area. B and C: after microsuperperfusion of the brain surface over the RVLM area with EPO, the IML neurons were depolarized (B) and the frequency of action potential (FAP) in the IML neurons increased (C). Open bar, before EPO superfusion; solid bar, after EPO superfusion; values are means ± SE. **P < 0.01 vs. before EPO superfusion. D: IML neuron at the Th2 level was hyperpolarized after SEPOR microsuperfusion over the RVLM area. E and F: after microsuperfusion of the brain surface over the RVLM area with SEPOR, the IML neurons were hyperpolarized (E) and the FAP in the IML neurons decreased (F). Open bar, before SEPOR superfusion; solid bar, after SEPOR superfusion; values are means ± SE. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. before SEPOR superfusion.