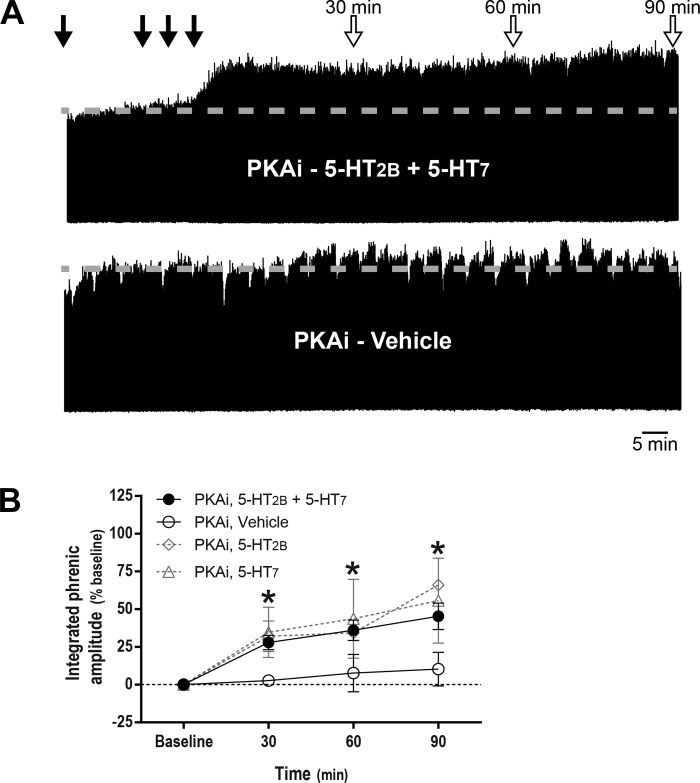
Fig. 4.
Protein kinase A inhibitor (PKAi) restores phrenic motor facilitation (pMF) after concurrent serotonin 2B receptor (5-HT2B) and serotonin 7 (5-HT7) receptor activation. A: representative traces of compressed, integrated phrenic neurograms at baseline, during and after intrathecal drug injections. Gray dashed line in each trace marks baseline amplitude of phrenic nerve activity. Top closed arrows depict intrathecal PKAi (1 mM, 10 μl) injections followed by episodic intrathecal drug injections; top open arrows on depict 30-, 60-, and 90-min blood samples. B: average (± SE) values from baseline to 90 min after episodic intrathecal drug injections (expressed as %baseline). Lines are from rats pretreated with intrathecal PKAi injections followed by either 5-HT2B (BW 723C86 hydrochloride; 1 mM) plus 5-HT7 receptor agonists (AS-19, 10 μM, 3 × 6 μl, n = 8) or vehicle (3 × 6 μl, n = 6). *Integrated phrenic nerve burst amplitude was significantly different from baseline and vehicle-treated rats at 30, 60, and 90 min post-5-HT2B and post-5-HT7 receptor activation. Magnitude of pMF at 90 min after either 5-HT2B (3 × 6 μl, n = 3) or 5-HT7 receptor activation (3 × 6 μl, n = 3) was unaffected by pretreatment with PKAi. Differences considered significant at P < 0.05. Mixed two-way ANOVA with repeated measures for time was used to detect overall differences between and within groups (interaction between time and groups was included in the model; F, 2.074; P < 0.05; df, 9), followed by Tukey's post hoc test.