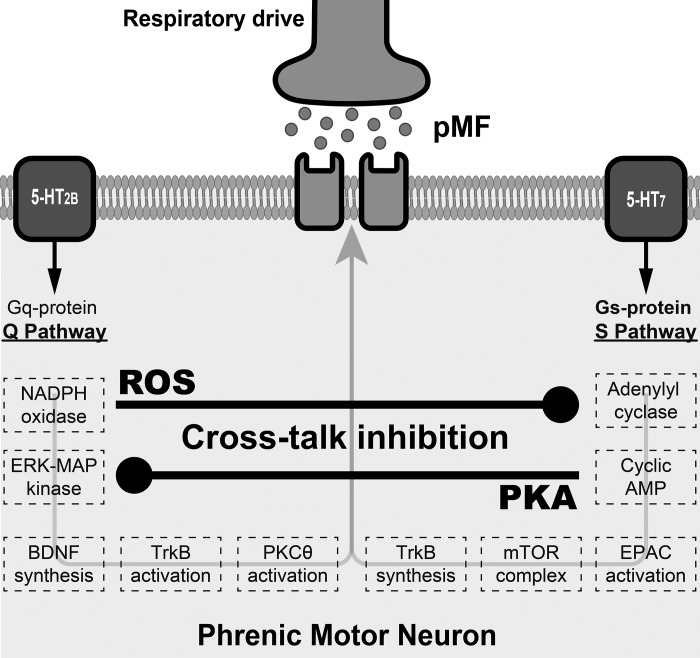
Fig. 5.
Schematic representation of multiple intracellular pathways independently leading to phrenic motor plasticity. Simultaneous pharmacological activation of the Q (5-HT2B receptors) and S (5-HT7 receptors) pathways abolishes phrenic motor plasticity via Q pathway-dependent NADPH oxidase activation and S pathway-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) activation. ROS, reactive oxygen species; BDNF, brain-derived neurotrophic factor; TrkB, tyrosine receptor kinase B; PKC, protein kinase C; EPAC, exchange protein activated by cAMP.