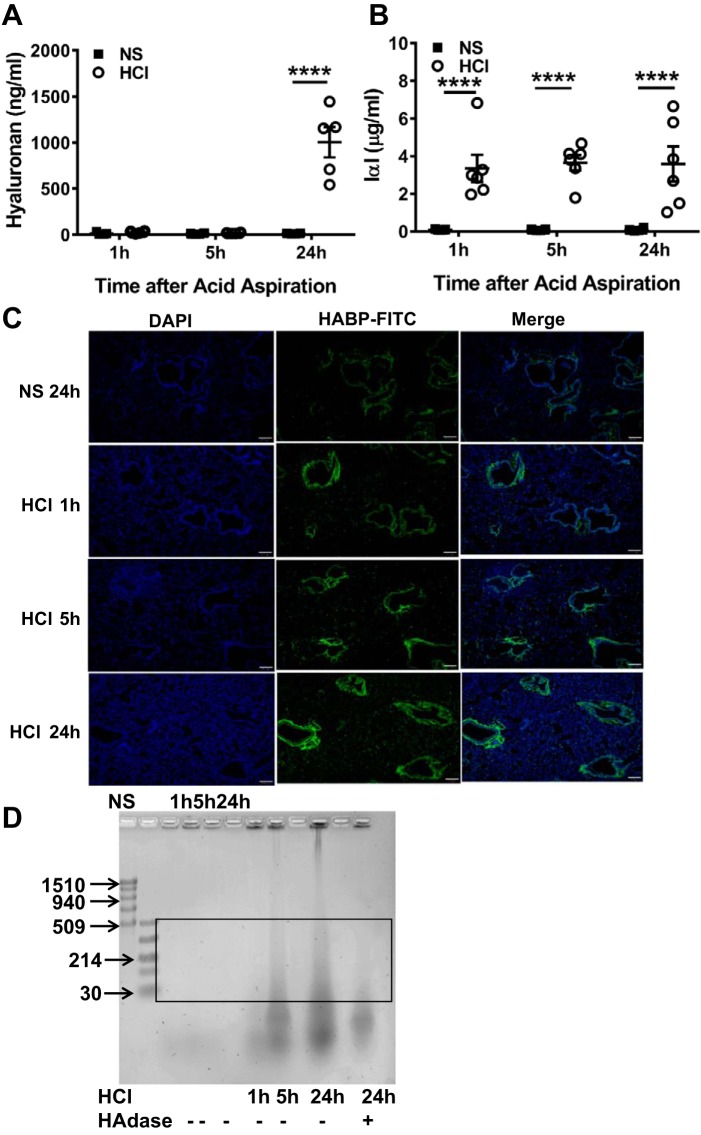
Fig. 2.
HCl instillation increases low-molecular weight hyaluronan (L-HA) in BALF and lung tissues. BALF hyaluronan (A) and inter-α-trypsin inhibitor (IαI) (B), a hyaluronan-binding partner protein, were measured by ELISA at 1, 5, and 24 h after HCl instillation. Each dot represents a different mouse; means ± SE. ****P < 0.0001, compared with corresponding NS control by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc comparisons; n = 5–6 for each group. C: FITC-labeled hyaluronic acid-binding proteins (HABPs) were detected in paraformaldehyde-fixed murine lung tissue at 1, 5, and 24 h post-HCl exposure and at 24 h after NS instillation as control. The level of HABP deposition in peribronchial spaces and alveolar/capillary septae increased with increasing time postexposure. Nuclei were highlighted with DAPI stain (blue). Scale bar = 100 µm. Characteristic images which were reproduced in 4 mice in each group. D: agarose gel image of BALF concentrate to detect HA. NS, normal saline; HAdase, hyaluronidase. Box area denotes L-HA; typical image was reproduced 4 times.