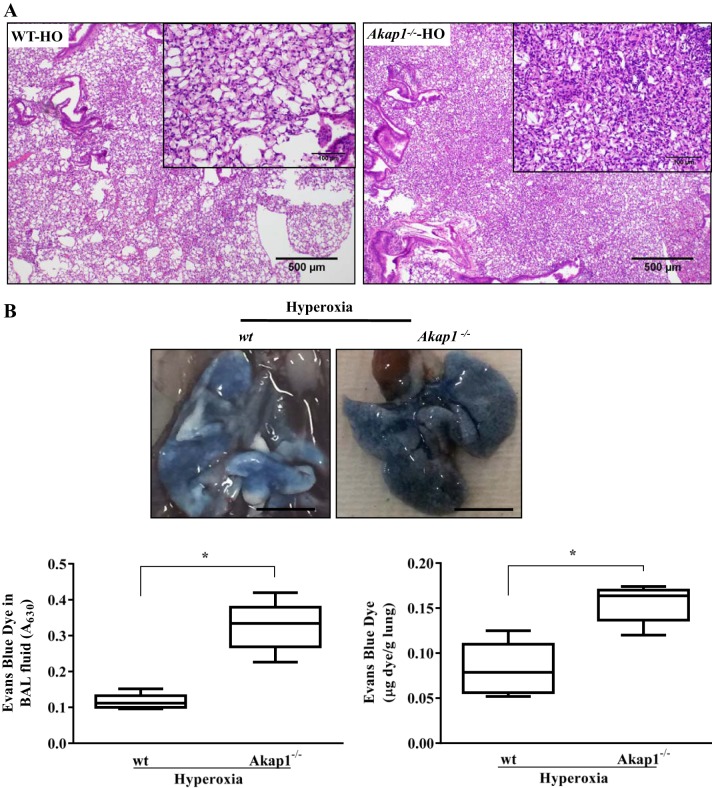
Fig. 3.
Akap1 genetic deletion increases lung injury and alveolar permeability after hyperoxia. Wild-type (wt) and Akap1−/− mice were exposed to hyperoxia (HO) for 48 h. A: Akap1−/− mice show increased damage against hyperoxia-induced ALI. Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) image has been shown from a total of 5 mice/group. The extent of lung injury was evaluated from H&E-stained lung tissue sections. Original magnification, ×40 (insets, × 200). B: extravasation of Evans blue dye (EBD) into the lungs following intravenous injection was photographed (top; scale bar = 1 cm) and quantified by spectrophotometry (bottom panel). BAL fluid (B, bottom left) and lung tissue (B, bottom right) EBD concentration. Data are shown as means ± SE (*P < 0.05 vs. wt hyperoxia; n = 5 mice/group).