Fig. 6.
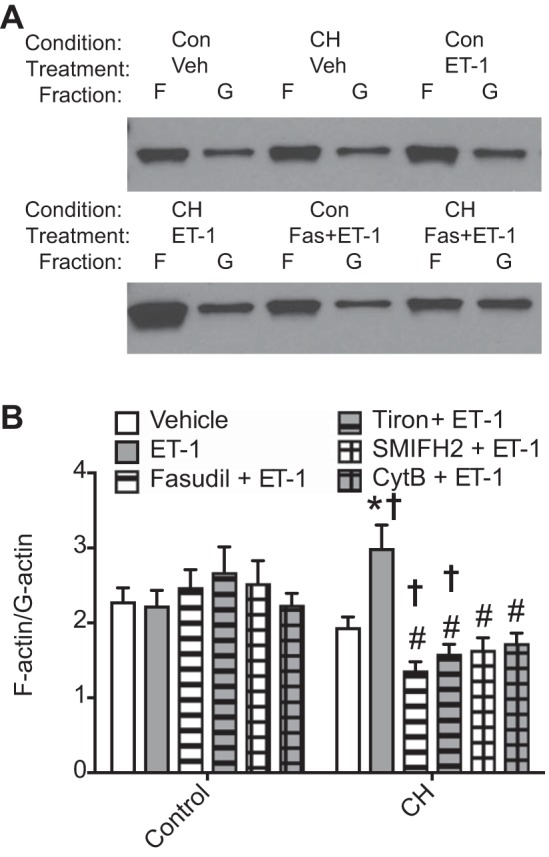
Chronic hypoxia (CH) augments endothelin-1 (ET-1)-stimulated actin polymerization in a Rho kinase-, reactive oxygen species-, and mDia-dependent manner. Intrapulmonary arteries from control (Con) and CH rats were treated with ET-1 (10 nM) or vehicle in the presence and absence of the following inhibitors: fasudil (Fas; 10 μM), tiron (10 mM), small-molecule inhibitor of formin homology domain 2 (SMIFH2; 20 μM), or cytochalasin B (CytB; 1 μM). A: Western blots were performed on fractionated lysates for which actin was probed. Representative blots showing actin in F-actin and G-actin fractions under indicated conditions. B: F-actin and G-actin were quantified by band intensity. n = 7–10/group. *P < 0.05 vs. CH vehicle; †P < 0.05 vs. the respective control; #P < 0.05 vs. CH ET-1.
