FIGURE 1. Patient 1, Time course of laboratory and histopathologic features in a patient with longstanding JAK2 V617F+ primary myelofibrosis who subsequently acquired BCR-ABL1. Temporary switch to chronic myeloid leukemia phenotype followed by Tyrosine kinase inhibitor induced reversion to primary myelofibrosis.
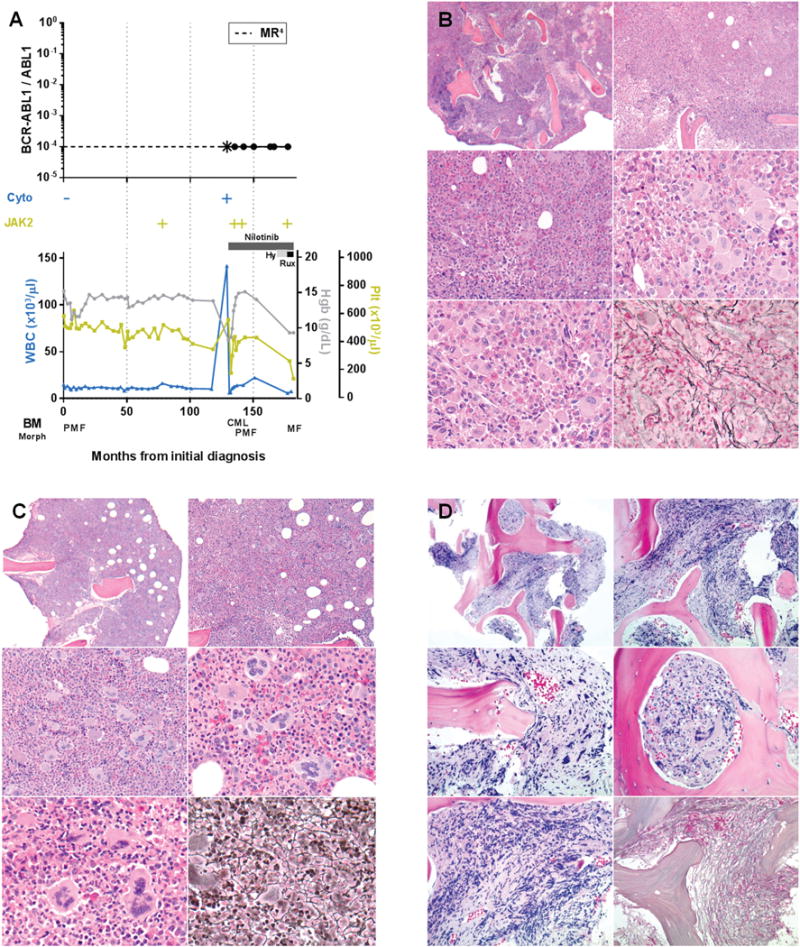
A. Time course of BCR-ABL1 transcript levels (log scale), cytogenetic t(9;22) results (Cyto), JAK2 V617F status, treatment, peripheral blood counts, and bone marrow morphology, Hy = hydroxyurea, Rux = ruxolitinib, *the first quantitative BCR-ABL1 assay performed after 3 months of tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy revealed that molecular response4 had been attained. B. Bone marrow core biopsy at identification of BCR-ABL1 (month 129) showing predominant features of chronic myeloid leukemia. Hypercellular (top), increased M:E ratio, increased hypolobated megakaryocytes with clustering (middle, bottom left), mildly increased reticulin fibrosis, grade 1/3 (bottom right). C. Bone marrow core biopsy after 6 months of tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy (month 135) showing predominant features of primary myelofibrosis. Hypercellular (top), mildly increased large megakaryocytes with bulbous nuclei (middle, bottom left), increased reticulin fibrosis, grade 1-2/3 (bottom right). D. Bone marrow core biopsy following tyrosine kinase inhibitor and hydroxyurea therapy (month 177) showing progression to fibrotic phase primary myelofibrosis. Focally hypercellular (top), increased hyperchromatic megakaryocytes (middle, bottom left), markedly increased reticulin fibrosis, grade 3/3 (bottom right).
