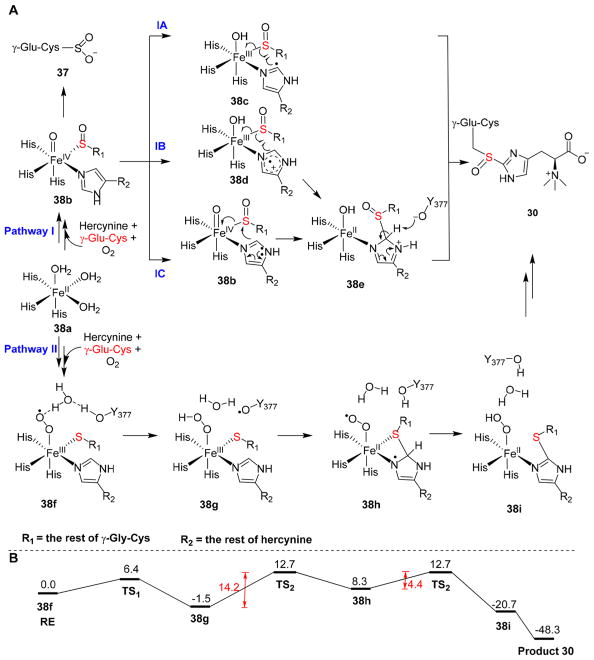
Figure 10.
Proposed mechanistic models for EgtB catalysis. (A) In pathway I, substrate binding and oxygen activation result in an Fe(III)–superoxo intermediate, which reacts with cysteine thiolate to form sulfenic acid and an FeIV═O species 38b. In this pathway, Y377 is proposed to function as a general base. In pathway II, after oxygen activation, FeIII–superoxo intermediate 38f oxidizes Y337 by a proton-coupled electron transfer process to generate a tyrosyl radical 38g. (B) Energy diagram of intermediates along pathway II in panel A based on quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics calculations.