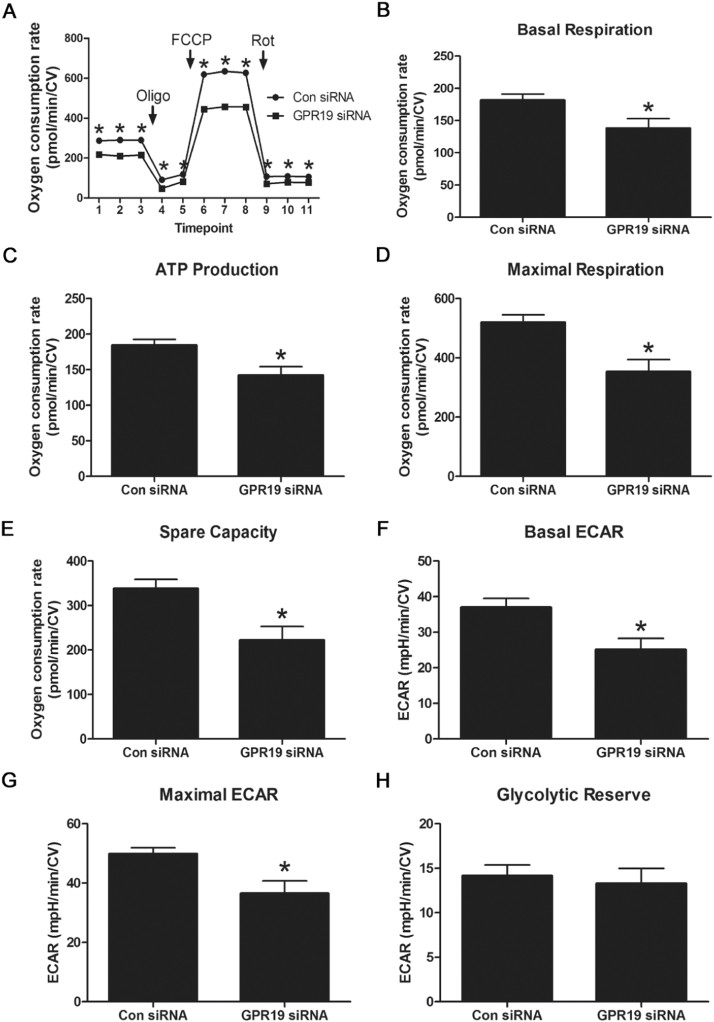
Fig. 3.
Genetic depletion of GPR19 blunts mitochondrial respiration. Knockdown of Gpr19 using siRNA in H9c2 cells led to a significant decrease in both basal and maximal mitochondrial oxygen consumption during Seahorse XF respirometry analyses (A-E). Loss of Gpr19 expression limited basal and maximal glycolysis, but had no effect on glycolytic capacity (F-H). N = 16–18, * = P < 0.05.