FIGURE 3.
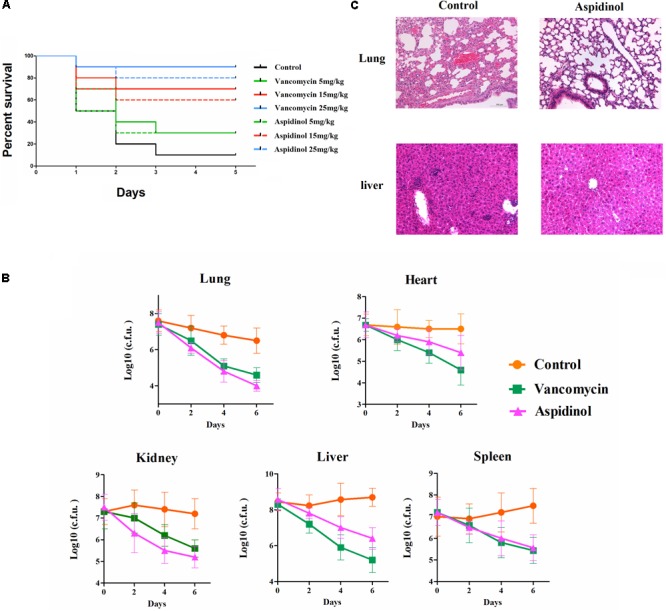
Aspidinol is effective in a mouse model of MRSA septicemic infection. (A) Ten mice per group were infected (i.p.) with a lethal dose of S. aureus ATCC 33591 and intravenously injected with aspidinol, vancomycin (5, 15, or 25 mg/kg), or the vehicle alone for 5 days (one dose per day). Mice were monitored for 5 days and the percentage survival was calculated. The statistical significance was calculated in order to compare treated to control groups. (B) Six mice per group were infected (i.p.) with a non-lethal dose of S. aureus ATCC 33591 and intravenously injected with aspidinol, vancomycin (25 mg/kg) or the vehicle alone for 6 days (one dose per day). Twenty-four hours after the last treatment, the mice were euthanized, and their organs were excised and homogenized in TSB to count viable MRSA colonies. The number of CFUs from each mouse is plotted as individual points. Values are the mean of triplicate samples with standard deviation bars. (C) Histological evaluation of lung and liver of mice infected with S. aureus ATCC 33591 receiving no treatment or a treatment with aspidinol. Both lung and liver in the control group demonstrated acute inflammation; no apparent pathological changes were observed in the treatment group.
