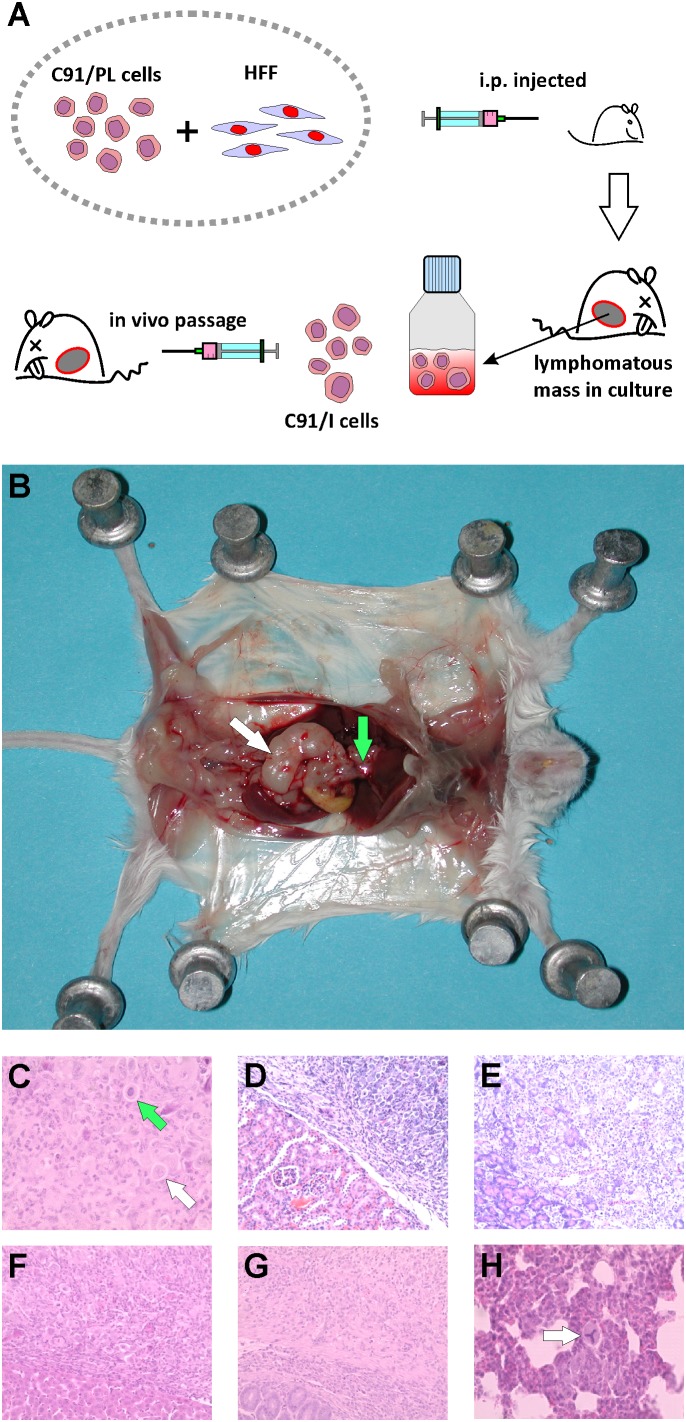
FIGURE 1.
Xenotransplantation of C91/PL-derived cell lines in Rag2-/-γc-/- mice. (A) Schematic representation of the in vivo experiments. C91/PL cells intraperitoneally co-injected with human fibroblasts into a 5-day-old Rag2-/-γc-/- mouse lead to lymphoma development. A fragment of the induced abdominal lymphomatous mass was processed under sterile conditions and cultured in vitro to establish a C91/PL-derived lymphomatous cell culture (C91/I). Injection of these cells into a Rag2-/-γc-/- mouse led to an aggressive Adult T cell Leukemia/Lymphoma (ATLL)-like lymphoma. Additional in vitro/in vivo passages were done with the establishment of two other lymphomatous cell lines (C91/II and C91/III). (B) Macroscopic view of lymphomatous masses developed in a mouse injected with C91/III cells involving mesenteric nodes (white arrow) and the liver hilum (green arrow). (C) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues shows tumor mass composed of pleomorphic cells mixed with syncytial cells (white arrow) with giant nuclei; the green arrow shows a pleomorphic cell with a giant nucleus. Original magnifications 400×. (D–G) Lymphomatous infiltration of kidney pericapsular area, pancreas, liver, and intestinal wall, respectively. Original magnification 200×. (H) Lung parenchyma with small embolic metastasis; arrow indicates abnormal tripolar mitosis. Original magnification 400×.