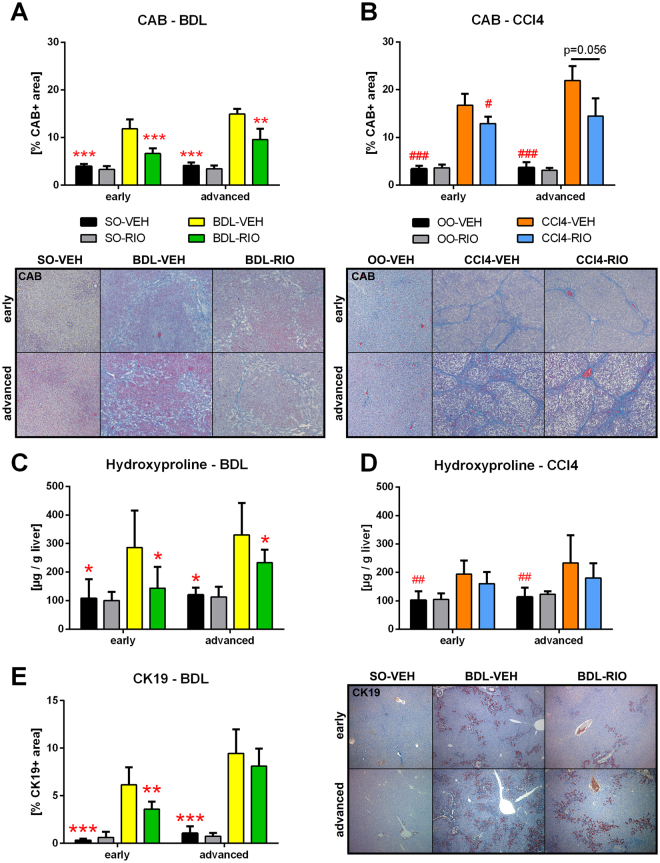
Figure 2.
Riociguat exerts antifibrotic activity in cholestatic and toxic models. (A) Hepatic chromotrope-aniline-blue (CAB) stained area was quantified to assess fibrosis. In early and in advanced BDL rats, RIO significantly reduced CAB stained area. (B) In CCl4 cirrhosis RIO reduced CAB area only in early but not in advanced disease. (C) The liver fibrosis marker hydroxyproline content was measured photometrically and corrected to liver weight. RIO reduced hepatic hydroxyproline in both, early and advanced BDL rats. (D) No differences regarding hepatic hydroxyproline content were notable in early or advanced CCl4 animals receiving RIO. (E) Cytokeratin-19 (CK19) immunohistochemistry staining of liver slides were quantified to determine bile ducts. In early BDL-RIO rats less biliary proliferation was notable. Representative liver slides are shown in panel A, B and E. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. BDL-VEH, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001 vs. CCl4-VEH; two-sided unpaired t-test; n = 5–8 per group in panel A, C and D - according to Table 1; n = 3–7 per group in panel B and D - according to Table 1.