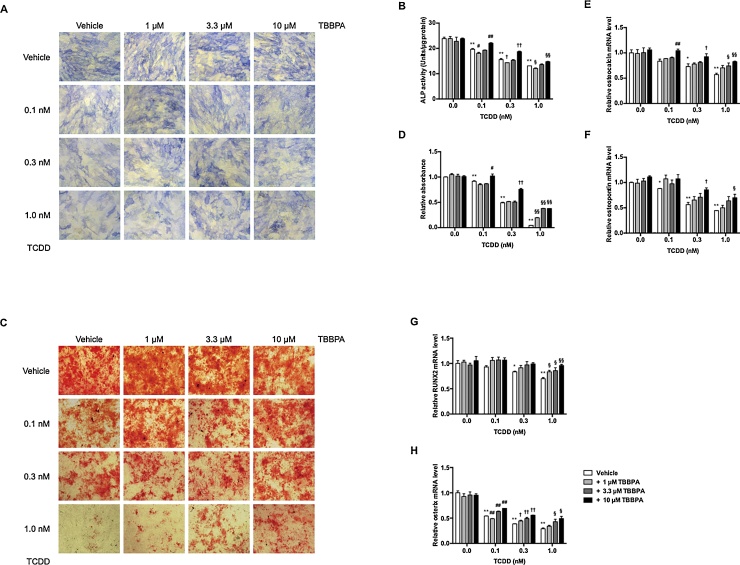
Fig. 2.
Effects of TBBPA and TCDD on osteoblast differentiation in hMSCs.
hMSCs were incubated with 1, 3.3, and 10 μM TBBPA and/or 0.0, 0.1, 0.3, and 1 nM TCDD for 14 or 21 days. At Day 14, ALP staining (A) and activity (B) were measured. At Day 21, calcium deposits were stained with alizarin red S (C). Morphological changes were observed under a microscope at 40× magnification. (D) Quantitative measurement of calcium deposites stained with alizarin red S. Alizarin red S in calcium deposites was eluted with 10% acetic acid. The relative absorbance at 450 nm was expressed as the fold induction as compared with the vehicle. At Day 21, osteocalcin (E), osteopontin (F), RUNX2 (G), and osterix (H) mRNA levels were measured by quantitative real-time PCR. The relative mRNA level was expressed as the fold induction as compared with the vehicle. The data are presented as means ± SD (n = 5). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with vehicle-treated cells in 0.0 nM TCDD. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, compared with vehicle-treated cells in 0.1 nM TCDD. †P < 0.05, ††P < 0.01, compared with vehicle-treated cells in 0.3 nM TCDD. §P < 0.05, §§P < 0.01, compared with vehicle-treated cells in 1.0 nM TCDD.