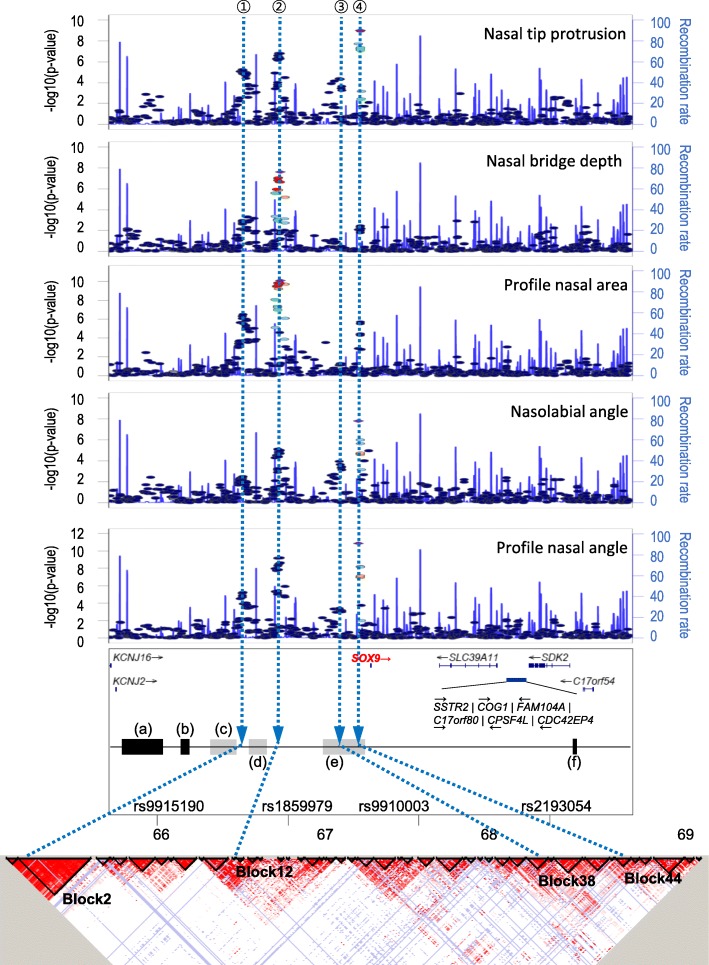
Fig. 4.
Association signals in the SOX9 locus and genomic environment surrounding SOX9 across a 4-Mb window. The upper five panels present multiple signals, (1) rs9915190, (2) rs1859979, (3) rs9910003, and (4) rs2193054, in the SOX9 locus for five nose traits: nasal tip protrusion [(H) prn-sn], nasal bridge depth [(H) n-prn], profile nasal area [(AR) n-prn-sn], nasolabial angle [(A) prn-sn], and profile nasal angle [(A) n-prn-sn]. These are plotted as −log10(P) against base-pair position on chromosome 17 (Mb) and all P-values are from the discovery phase. The sixth panel shows genes and regulatory domains. Gray boxes represent approximate boundaries of translocation breakpoint clusters, and black boxes represent microdeletions. (a) Sp4 [31], (b) F1 [31], (c) Pierre Robin sequence (PRS) breakpoint cluster [31, 32], (d) distal breakpoint cluster [30], (e) proximal breakpoint cluster [30], and (f) Sp2 [31]. The last panel presents LD blocks based on the HapMap database (HapMap Phase II JPT + CHB, hg18)