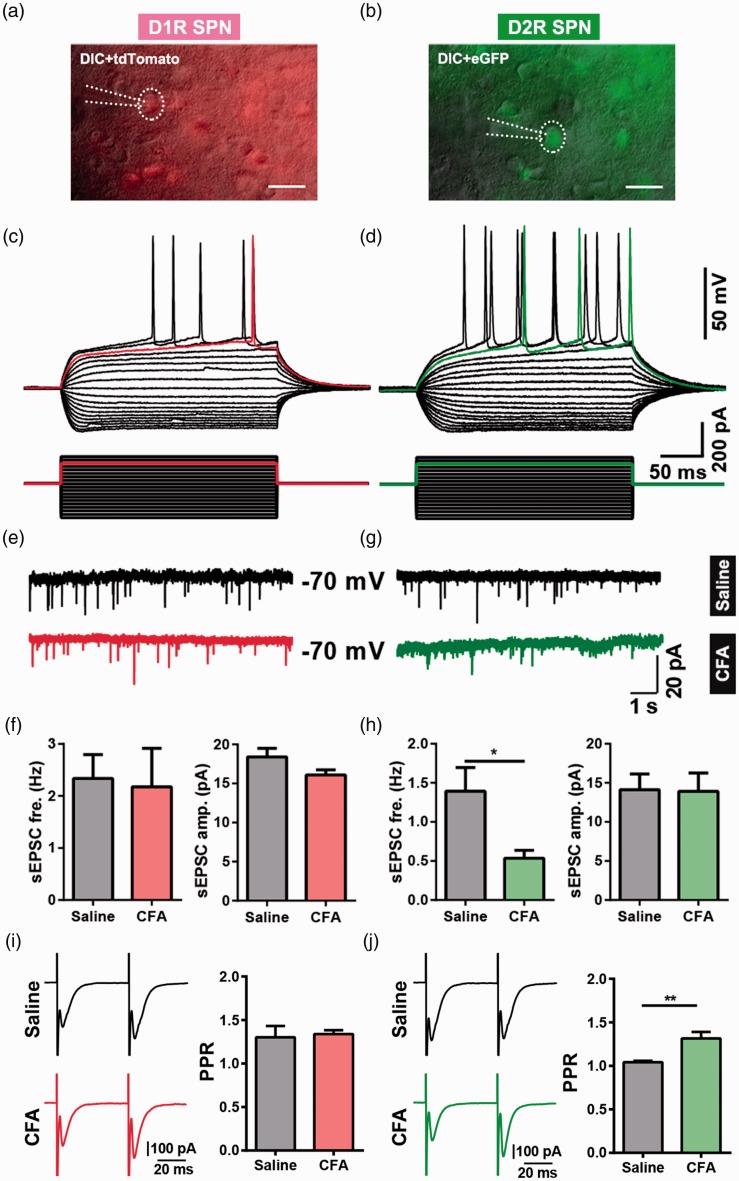
Figure 5.
Differential effects of CFA-induced chronic pain on glutamatergic synaptic transmission in D1R- and D2R-expressing SPN. (a) A Drd1-tdTomato-positive neuron (D1R SPN) was recorded by patch clamp pipette in differential interference contrast (DIC) image mode. Scale bar = 20 μm. (b) A Drd2-eGFP-positive neuron (D2R SPN) was recorded by patch clamp pipette in DIC image mode. Scale bar = 20 μm. (c) The same neuron from (a) showed a slow ramp depolarization and delay to the initial spike in current clamp mode. (d) The same neuron from (b) showed the typical delay firing pattern in current clamp mode. (e and g) Representative recording traces of sEPSCs of D1R SPNs (E) and D2R SPNs (g). (f and h) Summary data of sEPSCs frequency and peak amplitude in D1R SPNs (f: D1 saline group, n = 9; D1 CFA, n = 5) and D2R SPNs (h: D2 saline, n = 6; D2 CFA, n = 6). (i) Representative traces (left) and summary data (right) of paired-pulse ratio (PPR) of D1R SPNs from saline group and CFA group (D1R SPNs PPR: saline n = 6, CFA n = 8, p = 0.768). (j) Representative traces (left) and summary data (right) of PPR of D2R SPNs from saline group and CFA group (D2R SPNs PPR: saline n = 7, CFA n = 9, p = 0.0062). The data are presented as the means ± SEM, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, compared to the saline group.
CFA: complete Freund’s adjuvant; SPN: spiny projection neuron; D1R: dopamine receptor 1; D2R: dopamine receptor 2; sEPSCs: spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents; SEM: standard error of mean.n indicates the number of cells recorded.