Table 1.
Hypervalent iodine-mediated Ritter-type alkene oxyamidation.
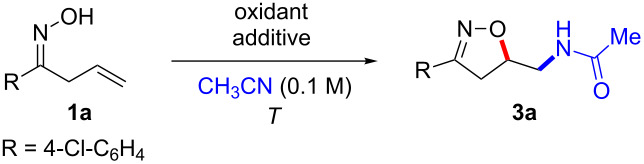 | ||||
| entrya | oxidant (equiv) | additive (equiv) | T (°C) | yield of 3a (%)b |
| 1 | – | BF3·OEt2 (1.0) | 25 | 10 |
| 2 | PhI(OCOCF3)2 (1.0) | BF3·OEt2 (1.0) | 25 | 35 |
| 3 | PhI(NPhth)2 (1.0) | BF3·OEt2 (1.0) | 25 | 42 |
| 4 | PIDP (1.0) | BF3·OEt2 (1.0) | 25 | 49 |
| 5 | PhI(OAc)2 (1.0) | BF3·OEt2 (1.0) | 25 | 55 |
| 6 | PhI(OAc)2 (1.0) | BF3·OEt2 (1.0) | reflux | 60 |
| 7 | IBX (1.0) | BF3·OEt2 (1.0) | 25 | 14 |
| 8 | DMP (1.0) | BF3·OEt2 (1.0) | 25 | 14 |
| 9 | PhI(OAc)2 (1.0) | AlCl3 (1.0) | 25 | 0 |
| 10 | PhI(OAc)2 (1.0) | SnCl4 (1.0) | 25 | 0 |
| 11 | PhI(OAc)2 (1.0) | TiCl4 (1.0) | 25 | 12 |
| 12 | PhI(OAc)2 (1.0) | TMSOTf (1.0) | 25 | 45 |
| 13 | PhI(OAc)2 (1.0) | – | 25 | 0 |
aAll reactions were performed on a 0.21 mmol scale (0.1 M) and with a standard 18 h reaction time. bIsolated yield.
