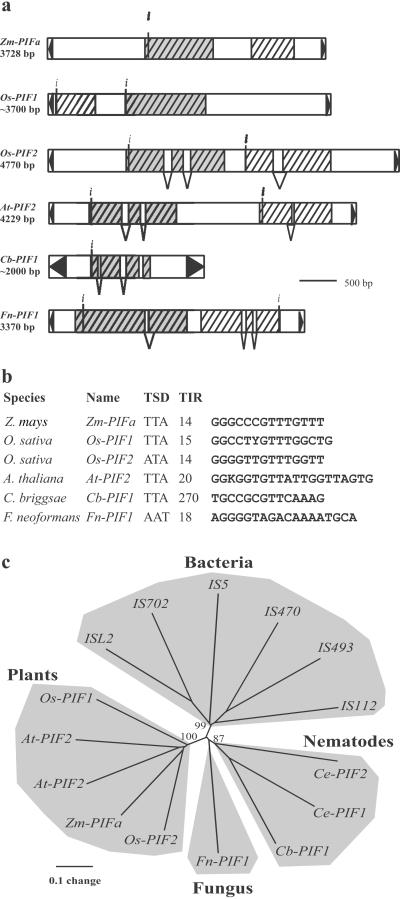
Figure 5.
The PIF-IS5 superfamily of transposons. (a) Structure and coding capacity of PIFa and several PIF-like elements. ORFs larger than 100 aa are schematically depicted as hatched rectangles. The predicted intron/exon structure is shown, as is the putative initiation codon (indicated by i). TIRs are represented by black triangles. Rectangles shaded in gray represent ORFs sharing significant similarity (i.e., PIF-like transposases). Other ORFs are not related, although the At-PIF2 downstream gene can encode a protein that has several paralogs in the Arabidopsis genome. However, these paralogous sequences are not associated with a PIF-like transposase (data not shown). In addition, Os-PIF1 and Cb-PIF1 contain nested insertions of a variety of repetitive sequences, thus making it difficult to unambiguously determine element length. For this reason, the length shown for these PIF-like elements is approximate. Species, GenBank accession numbers, and coordinates are: Zm-PIFa, Z. mays AF412282; Os-PIF1, Oryza sativa AC025098, 101769–109139; Os-PIF2, O. sativa AP01111, 2889–7665; At-PIF2, Arabidopsis thaliana TM021B04, 16996–21224; CbPIF1, Caenorhabditis briggsae AC090524, 69398–71455; Fn-PIF1, Filobasidiella neoformans AC068564, 3620–6989. (b) Putative TSD and terminal inverted-repeats (TIRs, size in bp) of PIF-like elements. (c) Phylogenetic relationship of putative PIF-like proteins and IS5 transposases. The unrooted tree was constructed with the neighbor-joining method from a clustalx alignment, which includes the complete product conceptually translated from the largest ORF of Zm-PIFa (313 aa), various eukaryotic homologs identified by database searches and several representatives of the IS5 group of transposases (ref. 29; see Fig. 6). Bootstrap values (1,000 replicates) support the grouping of the plant, nematode, and bacterial proteins. Ce-PIF2 is identical to the product recently reported as the Tc8.1 putative transposase by Le et al. (2001). Species and GenBank accession numbers are: At-PIF1, A. thaliana AB017067; Ce-PIF1, C. elegans CEF57G4; Ce-PIF2, C. elegans CELF14D2; IS5, Escherichia coli J01735; ISL2, Lactobacillus helveticus X77332; IS702, Calothrix sp. X60384; IS470, Streptomyces lividans AB032065; IS493, S. lividans M28508.