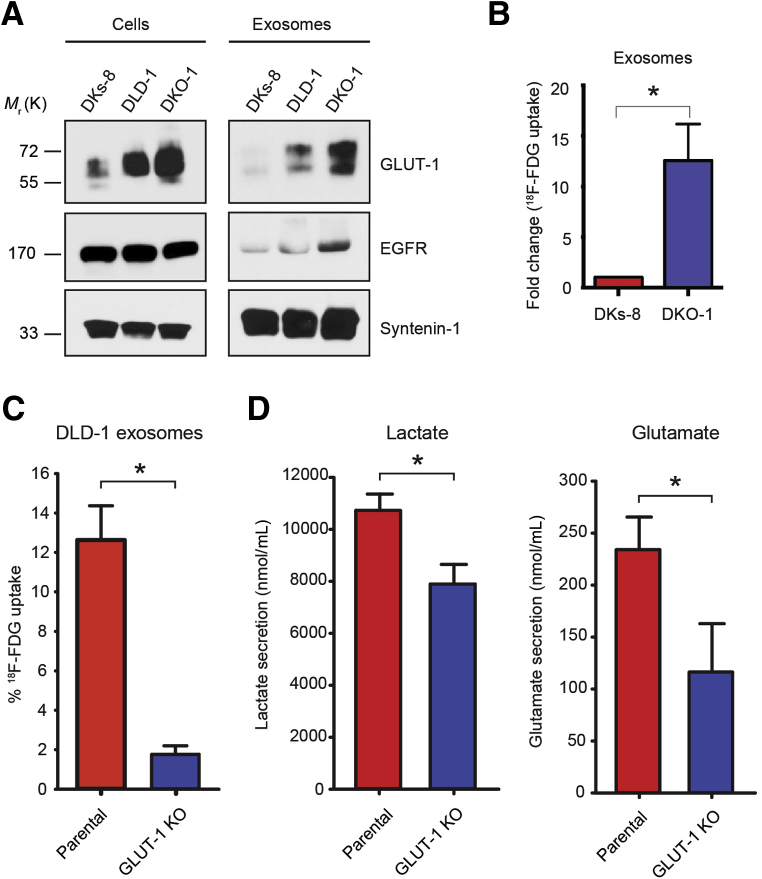
Figure 2.
Exosomal GLUT-1 partially drives metabolic changes in recipient cells. (A) Immunoblot analysis of cells and exosomes. After normalization to syntenin-1, levels of GLUT-1 were increased 2.5- and 3.1-fold in cell lysates and 3.1- and 5.2-fold in exosomes of DLD-1 and DKO-1 cells, respectively. (B) Percent 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18FDG) uptake in exosomes isolated from DKs-8 and DKO-1 cells (N = 3 in triplicate). (C) Fold-change of 18FDG uptake in exosomes isolated from parental and GLUT-1 KO DLD-1 cells. (D) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) determination of glutamate and lactate secretion in recipient DLD-1 GLUT-1 KO cells 43 hours after treatment with exosomes from parental DLD-1 or GLUT-1 KO cells (N = 2 in triplicate). Data are plotted as the means ± SD. *P < .05.