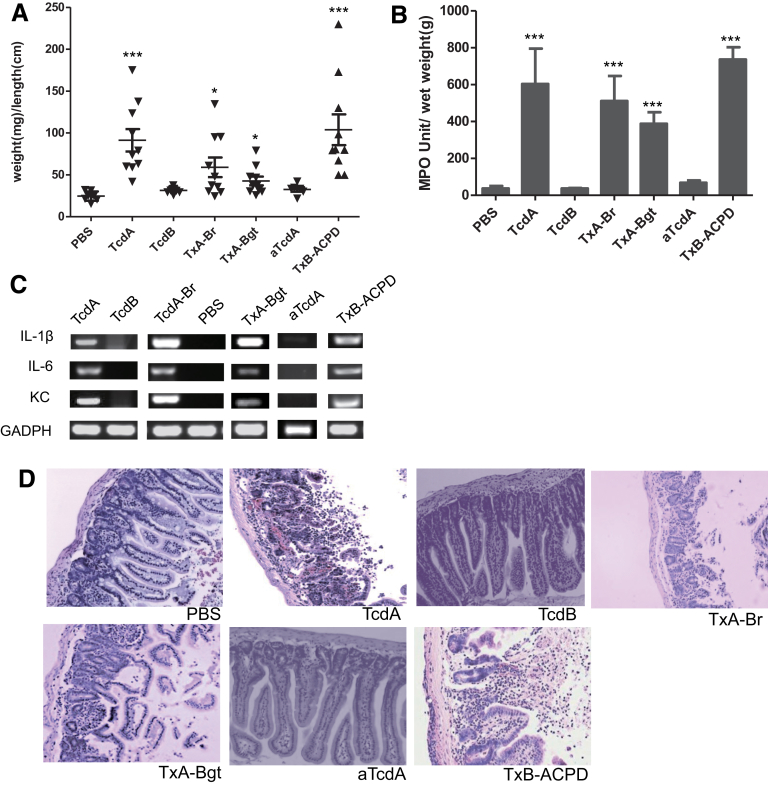
Figure 2.
Induction of acute inflammatory responses by wild-type and chimeric toxins. TcdA, TcdB, TxA-Br, TxA-Bgt, TxB-ACPD, or vehicle control (PBS) was injected into ligated ileal loops. The mice (n = 10) were killed 4 hours after injection and the ileal loops were collected for subsequent analysis. ***P < .001 (compared with PBS control). (A) Intestinal fluid accumulation was quantitated by the weight-to-length (mg/cm) ratio of the ileal loops. (B) MPO activity of the toxin-treated intestinal tissues. Intestinal tissues were homogenized to extract MPO and MPO activity units were calculated from a standard curve generated using purified MPO. (C) Messenger RNA expression of inflammatory cytokines in ileal tissues after PBS or toxin treatments. Semiquantitative reverse-transcription PCR was performed to detect the expressions of keratinocyte chemoattractant (KC), IL-1β, and IL-6 messenger RNAs. Equal loading was controlled by the amplification of the housekeeping gene glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). (D) Representative H&E-stained sections of treated ilea.