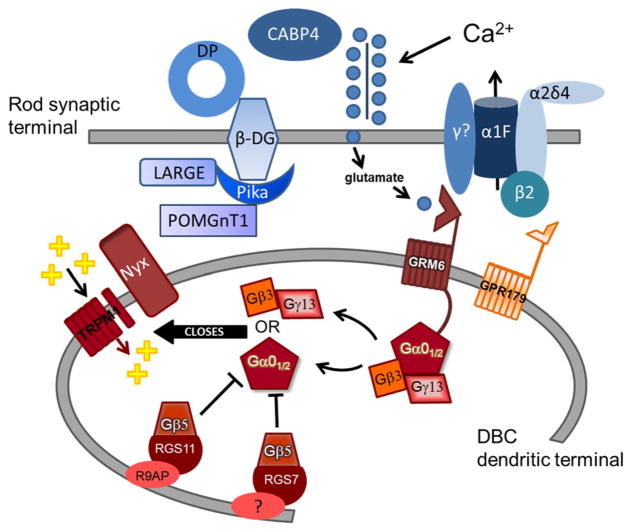
Fig. 1.
Diagram of molecules required for normal signaling between photoreceptors and DBCs. Pre-synaptic proteins (blue symbols) include the L-type voltage-dependent calcium channel composed of α1F, β2, γ, and α2δ4 subunits and the dystrophin–glycoprotein (DG) complex consisting of β subunit, the glycosyltransferase gene LARGE, pikachurin (Pika), Protein O-mannose beta1,2-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 1 (POM-GnT1), and dystrophin (DP). Post-synaptic proteins (red symbols) include metabotropic glutamate receptor 6 (GRM6), the orphan G-protein receptor GPR179, members of the G-protein regulating complex (Gβ5, RGS7, RGS11, and R9AP), G-protein subunits Gβ3, Gγ13, Gα01/2, the transient receptor potential melastatin 1 (Trpm1) cation channel, and nyctalopin (Nyx). Mutants for post-synaptic proteins lack the ERG b-waves, while this response component is reduced but retained in mutants for pre-synaptic proteins