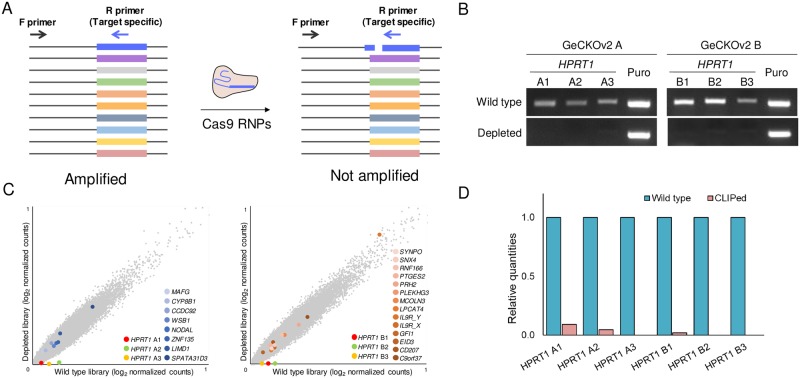
Fig 2. Cas9 RNPs treatment for the HPRT1-depleted CRISPR library generation.
(A) Schematic outline of PCR to assess the quality of the gRNA-depleted library. The forward primer annealed to the U6 promoter and the reverse primers could selectively anneal to the target sequences. While using the primer pairs, amplification occurred in the wild-type library, although not in the gRNA-depleted library. (B) The PCR amplicons of the HPRT1-depleted GeCKOv2 library were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. Each of the GeCKOv2 A and B libraries had three HPRT1 gRNAs, all of which were depleted from each library. For all six reverse primers annealed to the HPRT1 gRNA-encoding plasmid DNA, amplification occurred with the wild-type libraries as templates, although not with the HPRT1-depleted libraries. A pair of primers annealing to puromycin-encoding sequences in the plasmid DNA was used for internal control amplification. The primer sequences are listed in Table B in S1 File (C) Targeted deep sequencing analysis of the HPRT1-depleted libraries as described previously[11]. Scatter plots of the HPRT1-depleted GeCKOv2 A (left) and the HPRT1-depleted GeCKOv2 B (right) libraries showed that only HPRT1 gRNAs were depleted from the wild-type GeCKOv2 libraries. (D) Relative HPRT1 gRNA quantities were calculated from the targeted deep sequencing data. Numerical data are presented in S1 Table.