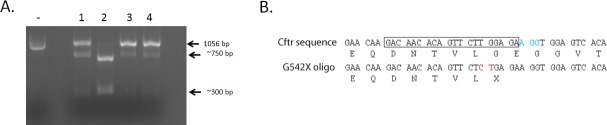
Fig 1. Generation of the G542X mutation.
(A) To validate gRNA efficiency in guiding Cas9 nuclease to the desired site, an in vitro assay was performed. PCR amplified DNA containing exon 12 and surrounding region of mouse Cftr (1056 bp) is displayed on an agarose gel with no gRNAs (-) or with 1 of 4 different gRNAs (1–4). Cas9 nuclease activity results in the cleavage of the DNA into fragments of ~750 bp and ~300 bp. (B) Normal Cftr mouse DNA and amino acid sequence around the desired mutation site is shown with the gRNA sequence (in box) and the protospacer adjacent motif sequence recognized by Cas9 (in blue). A portion of the sequence for the G542X oligo is also shown with the substitution change shown in red. The G to T mutation corresponds to the glycine to stop mutation. A silent T to C mutation was also inserted to assist with genotyping and verify HDR had occurred.