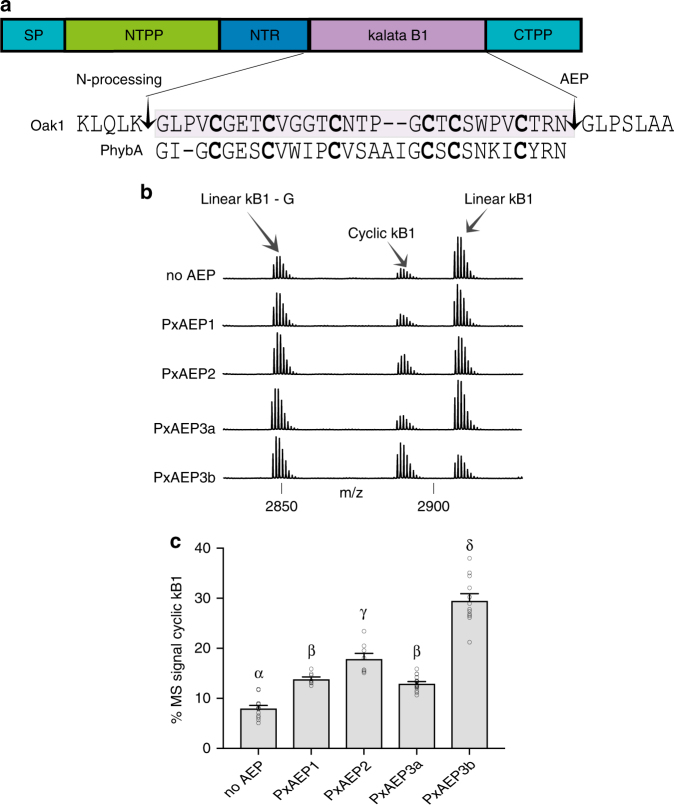
Fig. 1.
Petunia AEP isoform PxAEP3b functions as a ligase in planta. a Gene structure of Oak1, which encodes the prototypic cyclotide kB1 of O. affinis26. For maturation, the kB1 precursor is directed initially to the endoplasmic reticulum due to the presence of a signal peptide (SP). Here the precursor protein folds and disulfide bridges are formed. Further trafficking towards the vacuole facilitates resident proteases to release the amino terminal propeptide (NTPP) and amino terminal repeat (NTR). The liberation of the kB1 N-terminus is a pre-requisite for AEP-mediated backbone cyclization52. Shaded in purple is the 29 aa, six-cysteine containing kB1 peptide sequence. Flanking residues within the NTR and carboxyl terminal propeptide (CTPP) important for post-translational processing are shown. Aligned to kB1 is the Phyb A cyclotide from petunia, which could not be detected in N. benthamiana leaves despite co-expression of petunia AEP isoform PxAEP3b. Although similar in sequence, kB1 and Phyb A differ in topology with the presence of a cis-proline in kB1 leading to a conceptual twist in the cyclic backbone. b Representative MALDI-MS of kB1-related peptides produced upon transient gene expression in N. benthamiana leaves of Oak1 with or without co-expression of petunia AEP genes. c Mean and s.e.m of the percent MS signals obtained for cyclic kB1 over the total MS signal of all kB1-related peptides. Treatments carrying unique Greek lettering are significantly different (P < 0.05) as determined by Tukey’s ANOVA. Replicates are as follows: n = 14 (No AEP), n = 8 (PxAEP1 and PxAEP2), n = 16 (PxAEP3a) and n = 12 (PxAEP3b). Error bars are s.e.m.