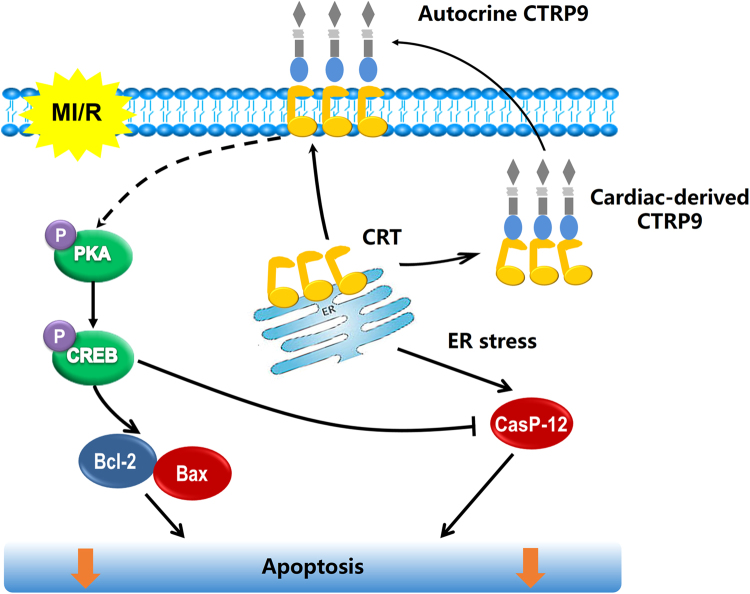
Fig. 8. Proposed mechanism responsible for autocrine CTRP9 of cardiomyocyte origin against MI/R injury.
Briefly, CTRP9 binds to ER molecular chaperone CRT in the cytoplasm of cardiomyocyte under physiological conditions. When subjected to MI/R injury, CRT translocates to cell surface and associates with autocrine CTRP9. CTRP9–CRT complex activates PKA-CREB pro-survival signaling and inhibits ER stress-related apoptotic signaling, directly protecting against MI/R injury