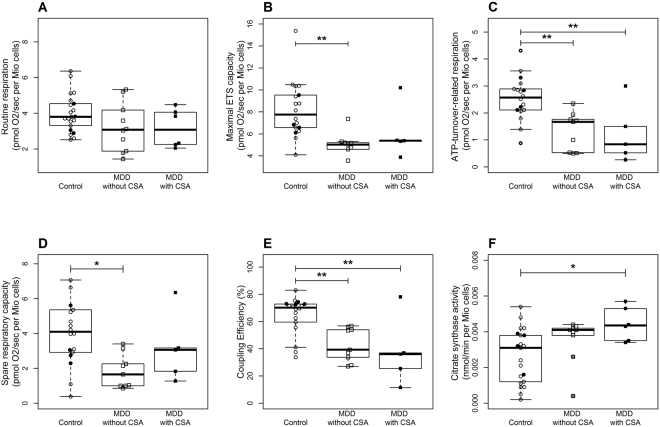
Figure 2.
Three-group comparisons of (A) mitochondrial routine respiration, (B) maximal ETS capacity, (C) ATP-turnover-related respiration, (D) spare respiratory capacity, (E) coupling efficiency, and (F) citrate synthase activity between non-depressed control subjects with (N = 4, filled circles) and without CSA (N = 17, open circles), MDD patients without CSA (N = 12, open squares), and MDD patients with CSA (N = 6, filled squares) revealed a stepwise decrease in ATP-turnover-related respiration and coupling efficiency with the strongest reduction in MDD patients with CSA, as well as an increase in the citrate synthase activity, with the highest values for MDD patients with CSA. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; CSA, childhood sexual abuse; ETS, electron transfer system; MDD, Major Depressive Disorder. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (Tuckey post-hoc comparisons).