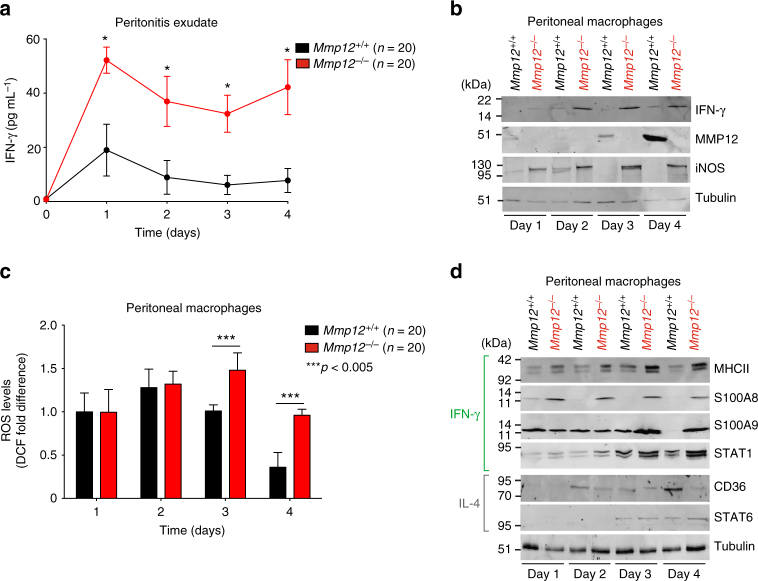
Fig. 3.
MMP12 decreases IFN-γ-activated macrophage markers in acute peritonitis. a ELISA of IFN-γ protein levels in peritoneal exudate of male Mmp12+/+ B10.RIII (n = 20) and Mmp12–/– B10.RIII (n = 20) mice at days 0–4 after induction of peritonitis (n = 4 for each genotype for each time point, N = 2) expressed as the mean ± s.d. There was no IFN-γ quantified in healthy peritoneum in the absence of inflammation on day 0. Statistical significance was determined by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test: *p < 0.05. b 10% SDS-PAGE western blot analysis of IFN-γ, MMP12, and iNOS proteins in primary peritoneal macrophages harvested daily from Mmp12+/+ (n = 20) and Mmp12–/– (n = 20) B10.RIII mice (N = 2). Tubulin, loading control. c Cellular ROS levels in primary peritoneal macrophages were quantified by calculating the mean fluorescence intensity after treatment with 2,-7-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCF) (n = 20 for each genotype, n = 4 for each time point, N = 2). Data were normalized to day 1 Mmp12+/+ B10.RIII macrophages and expressed as fold differences. Error bars, s.d. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test: ***p < 0.005. d 10% SDS-PAGE western blot analysis of markers characteristic for macrophage activation by IFN-γ (MHCII, S100A8, and S100A9) and STAT1, or by IL-4 (CD36) and STAT6 in Mmp12+/+ and Mmp12–/– B10.RIII mouse macrophages harvested daily (n = 20 for each genotype, n = 4 for each time point, N = 2). Tubulin, loading control. Molecular weight marker positions in all blots are as shown