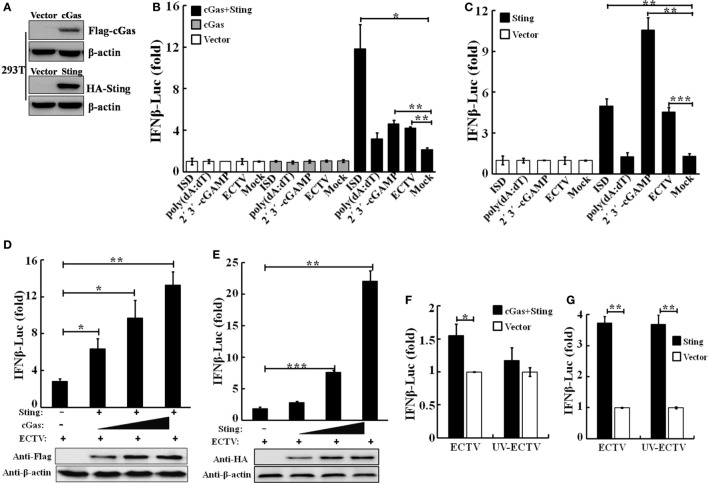
Figure 1.
Sting and cGas are required for the induction of IFN-β during ectromelia virus (ECTV) infection. (A) Overexpressed cGas, Sting, and β-actin protein levels in HEK293T cells were evaluated by Western blot. HEK293T cells (1 × 105) were seeded in a 96-well plate and then were transfected with pRL-TK Renilla luciferase reporter plasmid (10 ng/well), IFN-β firefly luciferase reporter plasmids (100 ng/well), and together with cGas (100 ng/well), Sting (100 ng/well), cGas + Sting (50 ng per plasmid per well), or vector only (100 ng/well) (B,C). After a 24-h transfection, cells were either stimulated with poly(dA:dT)/LyoVec (2 μg/mL), ISD/LyoVec (1 μg/mL), 2′3′-cGMP-AMP (cGAMP) (20 μg/mL), or infected with ECTV (MOI of 1) for 15 h, respectively. Luciferase activity was determined using the Dual-Glo® Luciferase Assay System. (D) HEK293T cells were transfected with Sting expressing plasmid (50 ng/well), and increasing doses of plasmids expressing cGas (25, 50, and 100 ng/well) combined with decreasing doses of vector (75, 50, and 0 ng/well). (E) HEK293T cells were transfected with increasing doses of plasmids expressing Sting (25, 50, and 100 ng/well) combined with decreasing doses of vector (75, 50, and 0 ng/well). After a 24-h transfection, cells were infected with ECTV at an MOI of 1 for 15 h. Expression of transfected cells with increasing doses cGas or Sting was examined by immunoblot analysis. HEK293T cells were transfected with cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) (50 ng) combined with Sting (50 ng) expressing plasmids (F) or Sting (100 ng) expressing plasmids (G), and 24 h later, cells were infected with ECTV and UV-inactivated ECTV at an MOI of 1 for 15 h. Luciferase activity was determined using the Dual-Glo Luciferase Assay System. All the data were averaged from three independent experiments in biological triplicate and represents mean ± SD. Statistical analyses were performed by a t-test (F,G) or one-way analysis of variance followed by the Duncan’s multiple range test (*P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; and ***P ≤ 0.001).