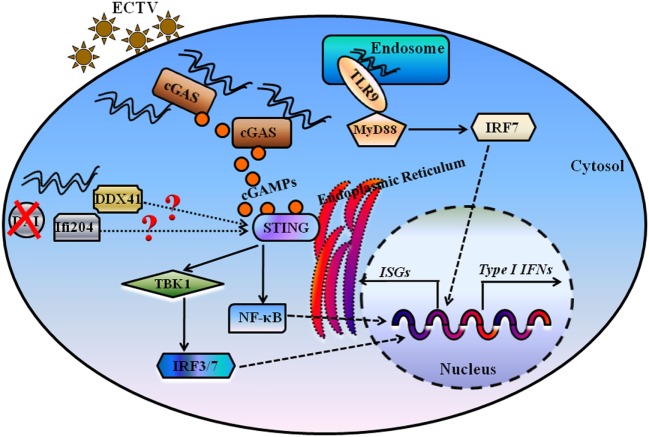
Figure 9.
Proposed model for illustrating the essential roles of DNA sensors in recognition and innate interferons (IFNs) production during ectromelia virus (ECTV) infection. Upon viral entry, some of ECTV virions are processed in the endosome, and viral DNA is firstly detected by Tlr9, which signals through the Myd88–Irf7 axis to promote expression of type I IFNs. Moreover, some of viral DNA is detected by the cytosolic DNA sensor cGas, and cGas catalyzes the formation of cGMP-AMP (cGAMP), which through the Sting–Tbk1–Irf3/7 axis leads to the activation of IFN responses. Other cytosolic DNA sensors, including Ifi204 and Ddx41, potentially recognize viral DNA present in the cytoplasm for the activation of IFN responses. DAI, one of the receptors upstream of Sting, has been ruled out as the critical DNA sensor for the activation of IFN responses during an ECTV infection.