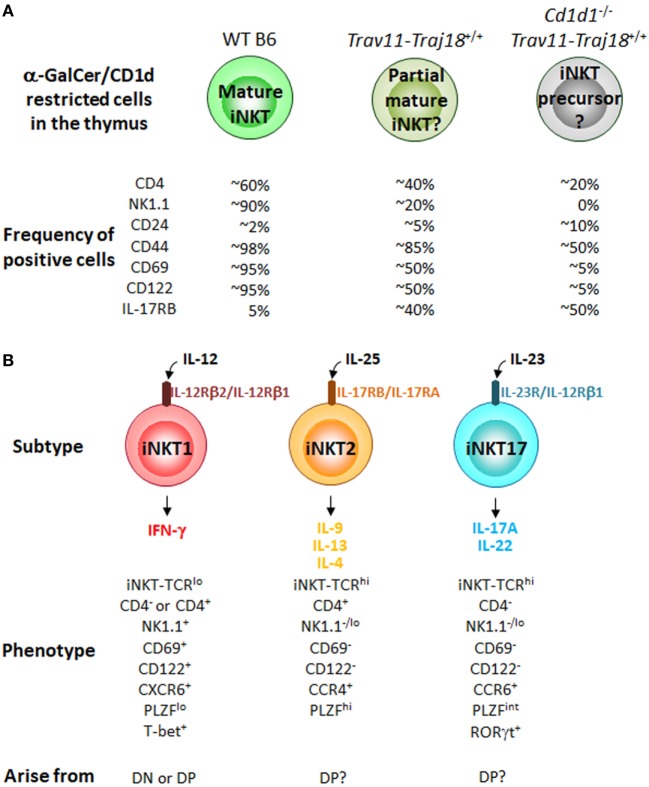
Figure 2.
CD1d restricted cells in iPSC-invariant natural killer T (iNKT)-derived cloned mice and iNKT cell subtypes in the thymus of B6 mice. (A) Percentage of CD1d-restricted α-GalCer/CD1d dimer+TCRβ+ cells positive for the indicated cell surface molecules in WT B6, Trav11-Traj18+/+ and Cd1d1−/−Trav11-Traj18+/+ mice. (B) The iNKT cell subtypes previously characterized in the thymus of B6 mice. Their phenotypes and developmental pathways in the thymus are also shown. Function of iNKT cells is acquired through the development in the thymus distinct from conventional αβ T cells. All of the iNKT subtypes may arise from the CD1d-restricted α-GalCer/CD1d dimer+TCRβ+ cells in Cd1d1−/−Trav11-Traj18+/+ mice in panel (A), while it still remains to be elucidated which signals control the divergence of iNKT1, iNKT2, and iNKT17 subsets.