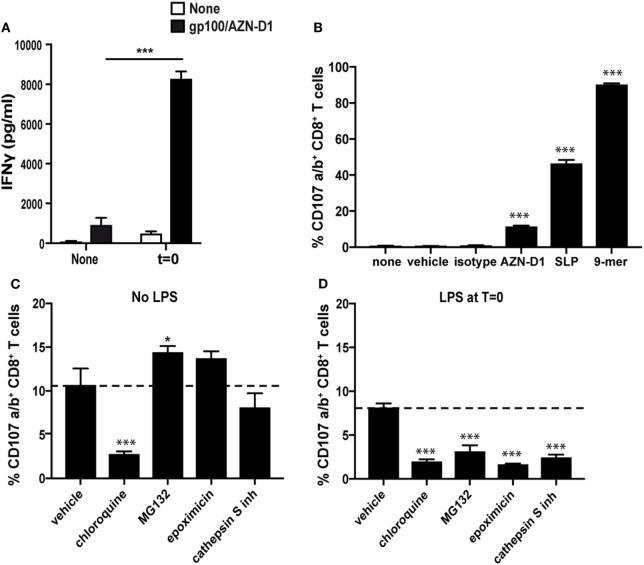
Figure 5.
Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) triggering facilitates antigen translocation to the cytosol. (A) Immature monocyte-derived DCs (moDCs) and moDCs that received a TLR4 stimulus at t = 0 [monophosphoryl lipid A (MPLA)] were pulsed with gp100/AZN-D1 for 3 h and subsequently co-cultured o/n with gp100280–288 CD8+ T cells. IFNγ secretion was analyzed by ELISA as a measure for T cell activation. (B) Immature moDCs were incubated with 0.1% DMSO (vehicle), gp100/AZN-D1 (10 µg/ml), gp100 synthetic long peptide (SLP) (10 µM), and the gp100280–288 9-mer minimal epitope (1 µg/ml) for 3 h. Thereafter, moDCs were co-cultured with gp100280–288 CD8+ T for 45 min and CD107a/b expression on the cell surface was analyzed as a measure for CD8+ T cell activation. Groups are significantly different compared to none, vehicle, and isotype. (C) Immature moDCs and moDCs that received a TLR4 stimulus [lipopolysaccharide (LPS)] at t = 0 (D) were incubated 30 min prior and during the 3 h antigen (gp100/AZN-D1) pulse with 0.1% DMSO (vehicle), chloroquine (25 µM), MG132 (10 µM), epoxomicin (0.25 µM), and cathepsin S inhibitor (5 µM). Groups are significantly different compared to AZN-D1. Data represented in mean ± SD, one-way ANOVA was performed, experiments are representative of a N = 2 for graph A and B and a N = 3 for graph C and D (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001).