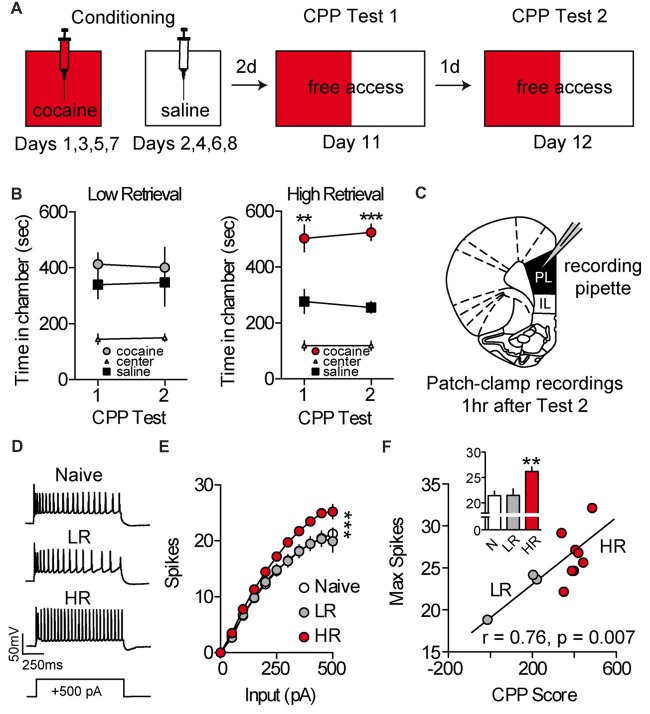
Figure 1.
Intrinsic excitability of prelimbic medial prefrontal cortex (PL-mPFC) pyramidal neurons is increased in HR rats. (A) Schematic showing design of conditioned place preference (CPP) conditioning and testing. (B) Line graphs revealing that LR rats did not express a cocaine CPP during first or second tests, whereas HR rats did express a cocaine CPP during both tests. (C) Patch-clamp recordings of layer V pyramidal neurons in PL-mPFC were taken from rats sacrificed 1 h after the second CPP test. (D) Representative waveforms showing 500 pA depolarizing sweeps from layer V pyramidal neurons. (E) Neurons from HR rats displayed more spikes at high depolarizing steps as compared with naïve and LR rats. (F) The maximum number of spikes that were fired on average in PL-mPFC pyramidal neurons from each rat correlated with CPP scores. Inset shows that the maximum number of action potentials that neuron would fire at any depolarizing step was higher in HR rats vs. neurons from naïve and LR rats. Line and bar graphs represent the mean ± SEM. HR, high retrieval; LR, low retrieval; **p < 0.01 vs. control; ***p < 0.001 vs. control.