Figure 1.
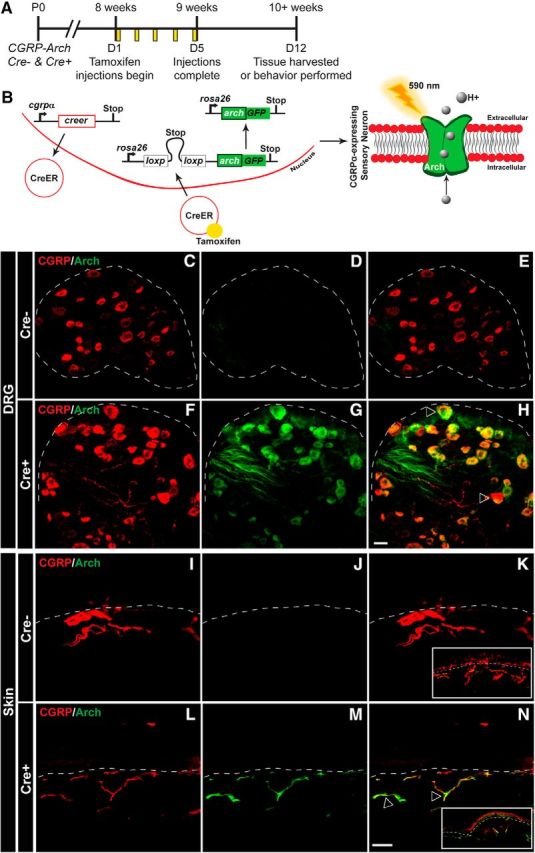
Generation of mouse expressing Arch-GFP selectively in CANs. A, CGRPα-CreER was induced with tamoxifen injections given once a day for 5 consecutive days in adult mice (8+ weeks). All experiments were performed at least 7 d after the last tamoxifen injection. B, Left, Schematic of CGRPα-CreER induction and removal of floxed stop codon, which subsequently drives the expression of Arch-GFP in CANs. Right, Arch is a proton pump that when activated by 590 nm light, pumps H+ ions out of the cell, and thereby hyperpolarizes the cell. C–H, Representative confocal images of lumbar DRG from CGRP-Arch Cre− mice (C–E) and Cre+ mice (F–H) stained with a CGRPα antibody (red) and excited Arch-GFP (green) with a 488 laser. Dotted line indicates border of DRG. C, F, Similar immunoreactivity was observed for CGRPα in both Cre− (C) and Cre+ (F) animals. D, G, Whereas negligible fluorescence was observed for Arch-GFP in Cre− animals (D), Arch+ fibers were observed throughout the DRG in Cre+ animals (G). E, H, Merged images showed no overlap between CGRPα and Arch-GFP in Cre− animals (E), but significant overlap in Cre+ animals (H). I–N, Representative confocal images of glabrous skin from CGRP-Arch Cre− mice (I–K) and Cre+ mice (L–N) stained with a CGRPα antibody (red) and excited Arch-GFP (green). Dotted line indicates epidermal/dermal border. I, L, CGRPα immunoreactivity was observed throughout neurons of the skin in Cre− (I) and Cre+ (L) animals. J, M, No Arch+ fibers were observed in Cre− mice (J), but many Arch+ fibers were observed in the skin of Cre+ animals (M). K, N, Merging showed no overlap between CGRPα and Arch-GFP in Cre− animals (K), but significant overlap in Cre+ animals (N). Inset, Image of skin at 6× lower magnification. Open arrows indicate examples of CGRPα and Arch-GFP overlapping expression. Scale bar, 25 μm. DRG marker quantification is shown in Table 1.
