Figure 5.
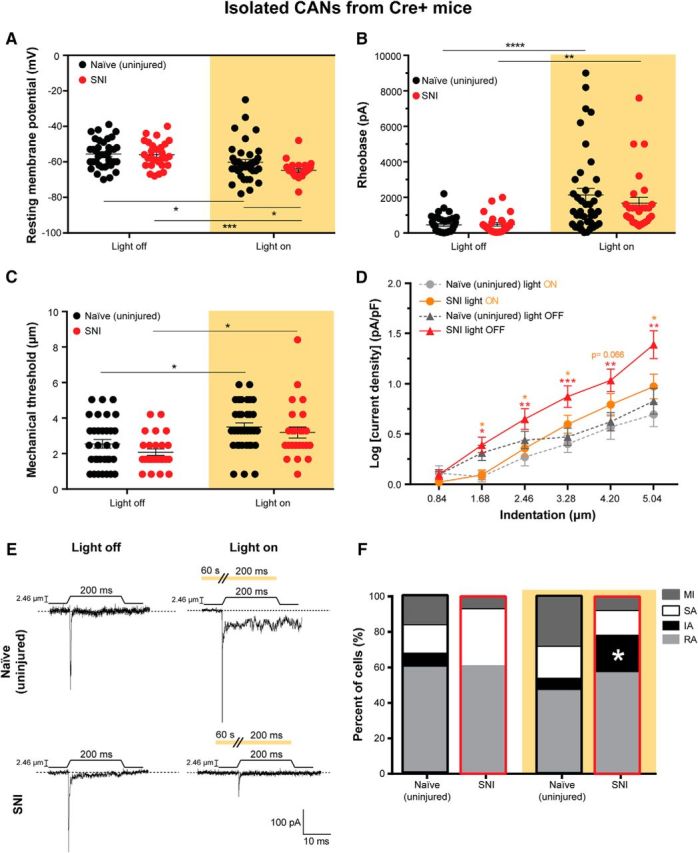
SNI increases mechanical responsiveness of CAN somata, which is reversed by Arch activation. Neurons from only the Cre+ CGRP-Arch mice were used for these experiments to be able to specifically identify CANs via their GFP expression. A, Resting membrane potential of naïve (uninjured) and SNI DRG neurons with (right) and without (left) Arch activation. Treatment of naïve (*p = 0.0254) and SNI (***p = 0.0002) neurons with 590 nm light decreased their resting membrane potentials compared with no light treatment. The 590 nm light decreased the resting membrane potential of the SNI neurons significantly more than naïve neurons (*p = 0.0474), two-way ANOVA. B, Rheobase (amount of current required to induce an action potential) in naïve and SNI neurons with (right) and without (left) Arch-activating light treatment. Treatment of naïve (****p < 0.0001) and SNI (**p = 0.0074) neurons with 590 nm light increased their rheobases compared with no light treatment, two-way ANOVA. C, Level of mechanical indentation required to elicit an inward current (mechanical threshold) in naïve and SNI neurons with (right) and without (left) light treatment. Treatment of naïve (*p = 0.0237) and SNI (*p = 0.0184) neurons with 590 nm light increased their mechanical threshold compared with no light treatment, two-way ANOVA. D, Log of mechanically gated current densities in response to a series of 6 increasing indentations of the DRG membrane of naïve neurons during light off (dark gray) and light on (light gray) and SNI neurons during light off (red) and light on (orange). Treatment of naïve neurons with 590 nm had no effect. SNI neurons had a greater current density in response to mechanical probing than naïve neurons. This increase in current density in response to mechanical probing in SNI neurons was reversed by 590 nm light treatment. Red asterisks indicate significant differences between naïve and SNI light off. Orange asterisks indicate significant differences between SNI light off and light on conditions. ***p < 0.0005 (mixed-model analysis). **p < 0.005 (mixed-model analysis). *p < 0.05 (mixed-model analysis). ns, Not significant (p > 0.05). E, Representative current traces from 2.46 μm indentation of naïve and SNI neurons during light off (left) and light on (right) conditions indicated by amber background. Amber bar above current traces during light on conditions (right) represents a continuous duration of light stimulation (60 s before the mechanical stimulus and throughout the 200 ms mechanical stimulus). F, Current kinetics in response to mechanical probing of naïve and SNI neurons during light off (left) and on (right) conditions. SNI neurons with no light treatment did not display IA currents, but SNI neurons treated with 590 nm light displayed a return of IA currents similar to naïve controls (*p = 0.0232). Black outline indicates naïve neurons. Red outline designates SNI neurons. Analysis was done using χ2 and Fisher's exact test. Amber background bars represent Arch-activating light treatment. Data are mean ± SEM. Naïve light off, n = 38 cells and n = 3 animals. Naïve light on, n = 40 cells and n = 3 animals. SNI light off, n = 28 cells and n = 6 animals. SNI light on, n = 28 cells and n = 6 animals.
