Figure 1.
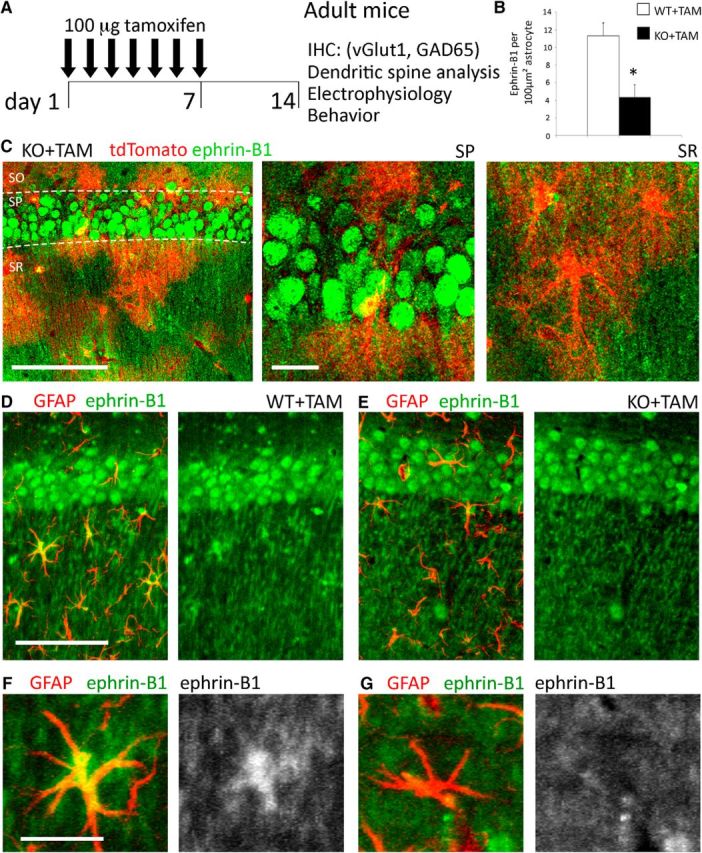
Tamoxifen-induced deletion of ephrin-B1 in the adult hippocampal astrocytes. A, Adult male ERT2-CreGFAP and ERT2-CreGFAPephrin-B1flox/y littermates (P90–P110) were intraperitoneally injected with 1 mg of tamoxifen once a day for 7 consecutive days. Immunohistochemistry, spine labeling, electrophysiology, and behavior tests were performed 14 d after first injection. B, Astrocytic ephrin-B1 immunoreactivity was significantly reduced in the hippocampus of KO+TAM compared with WT+TAM mice (n = 3 mice, t test, *p < 0.05). C, Max projection confocal images of the CA1 hippocampus in tamoxifen-injected ERT2-CreGFAPstopfloxtdTomato mice show tdTomato expression in astrocytes of SR, but not in CA1 neurons of the SP area. Ephrin-B1 immunoreactivity was detected in cell bodies (green, SP) and dendrites (green, SR) of CA1 neurons but not in tdTomato-positive astrocytes (red). Low-magnification. Scale bars: 100 μm; high-magnification, 20 μm. D, E, Max projection confocal images show GFAP (red) and ephrin-B1 (green) immunoreactivity in the CA1 hippocampus. Scale bar, 100 μm. F, G, High-magnification images show ephrin-B1 immunoreactivity in astrocytes of WT+TAM but not KO+TAM mice. Ephrin-B1 is detected in dendrites of CA1 neurons verifying that deletion of ephrin-B1 is specific to astrocytes. Scale bar, 25 μm.
