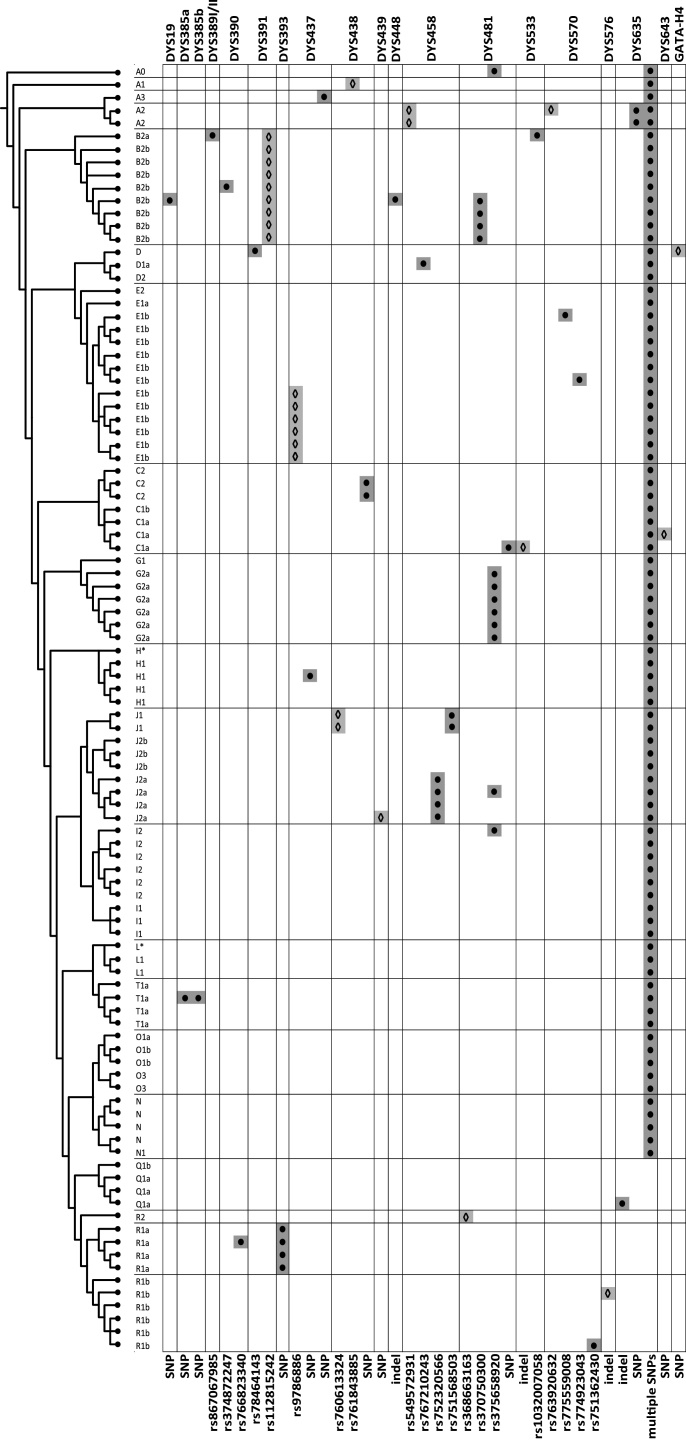
Fig. 1.
Observed SNPs and indels in their phylogenetic context.
The phylogenetic tree to the left represents the relationships among 100 diverse Y chromosomes, based on 13,261 high-confidence Y-SNPs previously described [11]. Y-chromosome haplogroups are given in their shorthand formats (Table S1) to the right of the tree. Y-STR names are listed above. Variants are shaded in grey and represented by filled circles if internal to the repeat array, or unfilled diamonds if in the flanking region. Variants are described below, by rs# where available, or otherwise as ‘SNP’ or ‘indel’ (Table S3). Note that ‘multiple SNPs’ internal to DYS635 (which we regard as an RPV − see text) are found in 85/100 samples because the GRCh38 reference assembly carries the same derived state as superhaplogroup P, and hence all deeper-rooting clades bearing the ancestral state are considered as ‘alternative’ rather than ‘reference’ variants. Note that rs370750300 and rs375658920 are listed elsewhere as DYS481-associated SNPs, and thus included in the figure; however, we regard these as an RPV (see text).