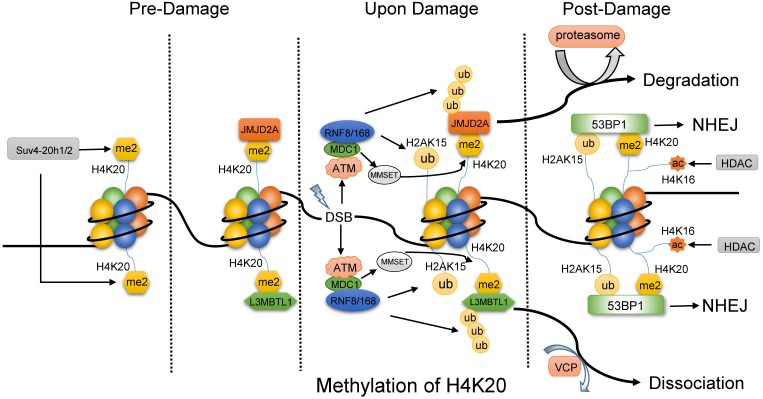
Fig 3.
The methylation of H4K20 might primarily favor NHEJ pathway. Before DNA damage, the di-methylated H4K20 by Suv4-20h1/2 is combined with L3MBTL1 and JMJD2A. Upon damage, ATM facilitates the recruitment of MDC1, and then MDC1 promotes RNF8 and RNF168 to accumulate at DSBs, which modify L3MBTL1, JMJD2A and H2AK15. Then, ubiquitylated L3MBTL1 is evicted by VCP and ubiquitylated JMJD2A is degraded by the proteasomes. In addition, phosphorylated MMSET by ATM is recruited to DSBs to mediate de novo dimethylation of H4K20 via binding to MDC1. As a result, 53BP1 is accessible to both the di-methylated H4K20 and ubiquitylated H2AK15 and initiate NHEJ pathway, while the deacetylation of H4K16 by HDAC might promote the binding of 53BP1.