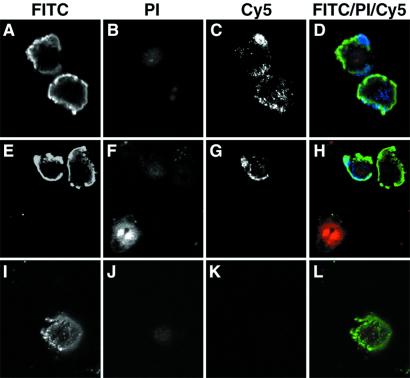
Figure 5.
Actin is exposed on the surface of apoptotic MCB cells, as determined by confocal microscopy. BrCaMz01 MCB cells induced with tumor necrosis factor α and cyclohexamide to undergo apoptosis were incubated with FITC-labeled annexin V (green), PI (red), and an anti-actin antibody or an isotype-matched control antibody (anti-FLAG tag) (blue). The anti-actin antibody (C and G) and the isotope control (K) were detected with Cy5-labeled anti-mouse IgG antibody. PI was included in all of the experiments to ensure the integrity of the membrane throughout the procedure and exclude the possibility that the anti-actin antibodies bound intracellular actin instead of cell surface-exposed molecules. Apoptotic cells were identified by the binding of annexin V to phosphatidyl-serine on the cell surface and the exclusion of the vital dye PI. As seen in D and H, the anti-actin antibody (blue) stained the cell surface of some of the apoptotic cells (green), whereas necrotic cells (H, Lower) only exhibited nuclear staining with PI (red), and healthy cells were not stained at all. In contrast, the isotype-matched control antibody exhibited no surface staining of the apoptotic cells (L).