Fig. 1.
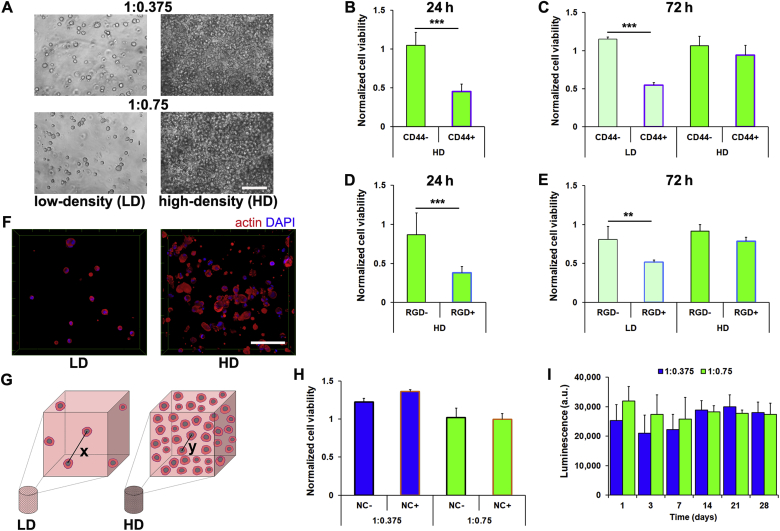
HD cultures do not rely on matrix cues or N-cadherin interactions to prevent anoikis. (A) Representative micrographs of hMSC (5 × 105 cells/mL (LD), 5 × 106 cells/mL (HD)) in 1:0.375 and 1:0.75 S-HA-PEGDA hydrogels after 24 h. (B) Viability of HD cultures of hMSC encapsulated within 1:0.75 hydrogels for 24 h and treated with anti-CD44 (CD44+) antibodies or isotype controls (CD44−) and normalized to vehicle controls, and (C) in both HD and LD cultures for 72 h (n = 3, ***P < 0.001). (D) Viability of HD cultures of hMSC in 1:0.75 hydrogels for 24 h and treated with RGD sequence-containing peptides (RGD+) or scrambled peptides (RGD-) and normalized to vehicle controls, and (E) in both HD and LD for 72 h (n = 3, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). (F) Representative micrographs of hMSC in LD and HD cultures for 72 h in 1:0.75 hydrogels stained with Phalloidin-TRITC. (G) Schematic highlighting theoretical distances between any two ‘nearest neighbor’ cells, where x = 69.8 μm and y = 32.4 μm. (H) Viability of LD and HD cultures of hMSC encapsulated in 1:0.75 hydrogels for 72 h and treated with anti-N-cadherin antibody (NC+) or isotype controls (NC-) and normalized to vehicle controls (n = 3). (I) Viability of HD cultures of hMSC in 1:0.375 and 1:0.75 S-HA-PEGDA hydrogels after up to 28 days (n = 3). In (A) and (F) scale bar = 100 μm. Plots show mean + SD. In (B)–(E) and (H) a two-tailed Mann-Whitney test, and in (I) a Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's Multiple Comparison were used to detect statistical significance.